Abstract
Introduction: Effectiveness of health education programme was evaluated among forty patients diagnosed as having fracture
and admitted at RLJH and RC with different types of orthopedic appliances.
Methodology: Using quasi experimental one group pre and post test design, patients were assessed for their knowledge
followed by a health education programme was administered on management of orthopedic appliances among fracture patients.
After seven days, a post test was conducted.
Findings: The results showed that structured health education programmed was effective in improving the knowledge score
among fracture patients on management of orthopedic appliances.
Conclusion: Health professionals should spend some time with fracture patient to educate regarding orthopedic appliances and
its related complications. So that, future occurrence of complications related to orthopedic appliances can be prevented.
Keywords: Knowledge; Health Education; Orthopedic Appliances; Fracture Patients
Introduction
Fracture is a disruption or break in the continuity of the bone.
It usually occurs as a result of blow to the body, a fall, or accident.
Traumatic injuries account the majority of the fractures, although
some fractures are secondary to a disease (pathological fractures).
The highest incidence of fracture in males is between the age
group of 15 to 24 years and in women it is 65 years or above [1].
Majority of patients with injuries of the musculoskeletal system
will be managed by bed rest, immobilization and rehabilitation
itself without requirement of surgical intervention. Immobilization
is achieved by orthopedic appliances. These appliances produce
skeletal changes by applying force with the help of plaster cast
and braces [2]. The patient with plaster cast may develop cast
syndrome due to obstruction of superior mesenteric artery and it
can be prevented if symptoms are recognized quickly and treatment
instituted in a timely manner. Expected complications of plaster of
Paris cast are impaired blood flow, nerve damage, tissue necrosis,
infection, cast syndrome and also other complications may arise
due to prolonged immobilization like hypostatic pneumonia,
foot drop, renal calculi, stiffness of joints, constipation, pressure
ulcer etc [3]. A study was conducted to assess the knowledge on
fracture among 127 osteoporosis patients with recent fragility
fracture at Hamilton Health Sciences hospital. The results showed
that, majority of patients were unaware of important risk factors
related to fracture. The study concluded that education initiatives
are essential in improving knowledge among individuals in
fracture clinics, acute care and rehabilitation settings, as these
areas are an ideal place to communicate information [4]. Majority
of musculoskeletal disorders are relatively long time in nature.
The care and management of this condition needs a specialized
orthopedic nursing practice5. After going through the related
literature it was found that there were no studies either in India
or abroad specifically related to management of orthopedic
appliances. Hence the researcher felt with an objective to evaluate
the effectiveness of structures health education programmed on
management of orthopedic appliances among fracture patients.
Materials and Methods
This study was based on Ludwig Von Bertalanff’s general system
theory. The design used for the study was quasi experimental
one group pre test and post test. Based on the objectives of the
study, a structured knowledge questionnaire and a lesson plan of
health education on management of orthopedic appliances among
the fracture patients was prepared in English and then it was
translated to Kannada since the study participants communication
and understanding were only in Kannada. Later the tool and health
education lesson plan was validated by eight research and subject
experts for its adequacy and appropriateness. After obtaining
an ethical clearance from an institutional ethical committee, a
written consent was obtained from the Medical Superintendent
of RL Jalappa hospital and research centre, Tamaka, Kolar. After
taking consent from the patients, through simple random sampling
technique lottery method, 40 patients were selected who were
diagnosed as having fracture and admitted to hospital with different
orthopedic appliances, with the age group of 20 to 60 years, able
to communicate with kannada or English language and willing to
participate in the study. Patients who were critically ill, developed
complications during the study period and mentally challenged
were excluded from the study. Then the data was collected by using
structured knowledge questionnaire on management of orthopedic
appliances. Followed by on the same day, a health education
on management of orthopedic appliances were administered
using chart, flash card, pamphlet and OHP by individually and in
groups. After seventh day, post test was conducted using same
questionnaire. The data was collected from 26th June 2014 to 30th
July 2014 in orthopedic wards.
Results
Socio-demographic variables
Table 1 displays socio-demographic variables of fracture
patients. The majority( 37.5%) of fracture patients in this study
were in the age group of 20-30 years and 30% of them with age
group of 51-60 years, most(55%) of them were males, 70% of them
were married, 70% of them were Hindus, 80% of them were belong
to rural area, 32.5% of them were studied up to high school, 65%
of them were belong to joint family, 52.5% were coolie workers
and 40% of fracture patients family income was below Rs.5000/-
month.
Knowledge score of fracture patients
After obtaining socio-demographic data, the fracture patients
were assessed for their knowledge score on management of
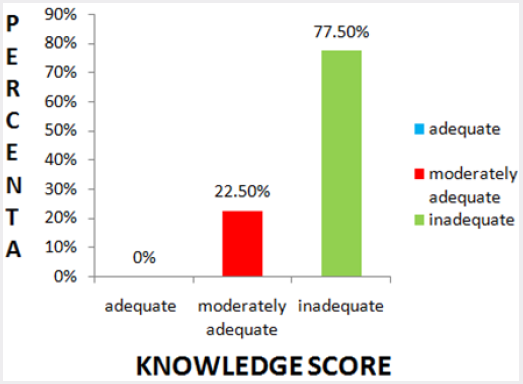
orthopedic appliances and presented in Table 2. Based on overall
knowledge score obtained by fracture patients, they were grouped
under inadequate knowledge (who scored below 50%), moderately
adequate knowledge (who scored 50 to 75%) and adequate
knowledge (who scored 76% and above) and presented in Figure 1.
Table 1: The Socio-demographic variables of fracture patients.

Table 2: Area wise pretest mean Knowledge score distribution
of fracture patients.
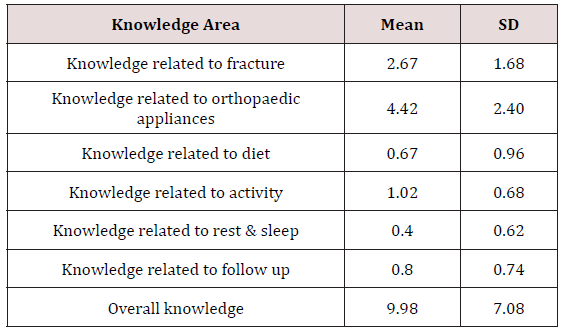
Figure 1: Distribution of fracture patients based on their
Knowledge score.
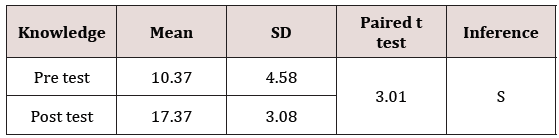
Effectiveness of health education programmed in
improving knowledge score
After administering health education programmed, a post
test was conducted to know the effectiveness of health education
programmed on management of orthopedic appliances and the
results revealed that, the pre test mean knowledge score was 10.37 with
SD of 4.58 where as the mean post test knowledge score was
17.37 with SD of 3.08, while enhancing the mean knowledge score
of 7. The obtain t value was 3.01 which was significant at 0.05 level.
This indicated that health education programmed was effective in
increasing the knowledge score among fracture patients and the
same was presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Comparison of overall pre and post test knowledge
scores of fracture patients.
Association of knowledge score with selected sociodemographical
variables
The association between post test knowledge score of fracture
patients with selected socio demographic variables revealed
that, there was no association between gender (x2=0.22), religion
(x2=1.13), educational status(x2=0.02), type of family(x2=3.53 ),
occupation (x2= 3.52) and family income (x2=0.6) except age in
years(x2=7.91) which was significant at 0.05 level.
Discussion
Knowledge regarding management of orthopedic appliances
among fracture patients is very essential in preventing complications.
Hence the study was undertaken to assess the effectiveness of
health education programme on knowledge regarding management
of orthopedic appliances among fracture patients and the results
showed that, with regard to socio-demographic variables, majority
(37.5%) of them were in the age group of 20-30 years and most
(55%) of them were males which was contradicted by the study
conducted by Swati Kambli [6]. Related to knowledge score, the
mean pre test knowledge score was 10.37 with SD of 4.58 where
as the mean post test knowledge score was 17.37 with SD of 3.08,
while enhancing the mean knowledge score of 7, indicating that
health education programme was effective in improving knowledge
score among fracture patients and this was supported by the study
conducted by Saccone M, Jain AK [7]. With regard to association
of knowledge score with selected socio-demographic variables, it
was found that there was no association between knowledge with
selected socio demographic variables except age.
Limitations
The study was limited to fracture patients admitted at RL
Jalappa Hospital and Research centre, with different orthopedic
appliances.
Conclusion
The present study concludes that, structured health education
programme was effective in improving the knowledge score among
fracture patients on management of orthopedic appliances.
Acknowledgement
Researcher expresses her sincere gratitude to all fracture
patients who participated in the study and authorities of RL Jalappa
hospital for granting permission to conduct the study.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.