Lupine Publishers | LOJ Medical Sciences
Abstract
The author presents the physical structure of the light cone, which
divides the space-time into two parts. The information and
events in the first one is connected with each other and may form the
cause-effect chains. The information and events in the other
one (dubbed “elsewhere”) cannot influence the run of events under
consideration. The same general philosophy might be applied
to the motor operation patterns in humans (and other living beings)
while taking into consideration temporal constraints of various
rungs of the modalities’ ladder. The latter is a mental structure
originated in N.A. Bernstein’s “brain skyscraper”. Author shows at the
practical manifestations of the application of the mental model termed
events’ cone.
Keywords: Anthropokinetics; Modalities’ ladder; Light cone; Events’ cone
Introduction
Let us start from three simply banal statements:
A. Firstly: The only manifestation of any mental activity,
and the only way to affect the environment, is the movement.
Consequently, there are no other behaviors than the motor ones.
B. Secondly: The main task of the Science (with great “S”)
probably most consciously has been expressed by Auguste Comte
in the words “To know in order to predict; to predict in order to
can” [1]. The first element of this statement may be substituted
with the word “understand”. If one wants to predict, it is not
enough to simply know; it is necessary to understand the essence
of phenomena and processes under consideration and their mutual
relations. The accurate prediction causes-nearly directly-the
potentiality of realization of actions reliably resulting with desired
effects. In general, “to understand” (or, may be, more precisely- “to
grasp”) might be regarded as a product of philosophy, “to predict”-a
product of science, and “can”-a product of technology.
C. Thirdly: Let us remember that mathematics is the science
on relations, which facilitate understanding. In the non-living
world, where the things passively obey the laws external against
them, establishing of the net of such laws enables predicting the
behavior of such things also in the future. On the other hand, in the
living world the laws are not external against the entities (no longer
“things”!). In biology, just these entities contribute to creation of
such relations. More, in psychological processes, where various
relations are being actively and sometimes “online”, i.e., consciously
shaped by living entities. Not rarely such relations act only in very
short periods. Therefore, it is not possible to establish a universal
net of relations, reliably governing the behavior of living entities.
Therefore mathematics-being the science on relations, which may
be described with a “stiff” formalism-is not eligible for description
of biological phenomena, where the evolution destroys any
“stiffness” of a formalism (or any “formalism-like” structure). The
same concerns, more, the psychological processes, which are not
prone to any “formalism-like” constraints, external against entities
being described and taking no into consideration their internal
determinants [2,3].
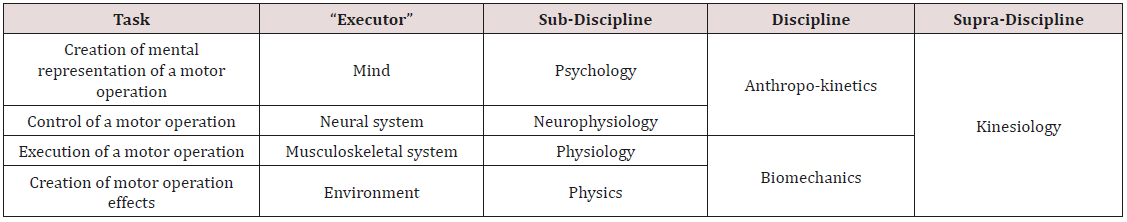
The term “anthropokinetics” from the title of this paper should
be described more precisely. The position of this discipline in the
general system of sciences on human motor behavior has been
shown in the Table 1. It is worth noting that specific disciplines,
which in such a system have been termed “sub-disciplines”, in
other systems may play the function of supra-disciplines. Such a
flexibility makes one of the aspects of beauty and usefulness of a
system. However, in the system of sciences on motor behavior such
an order seems to be the most effective.
Table 1: The system of sciences on motor behavior of living beings, especially humans (Petryński, 2019, in print).
The physical light Cone
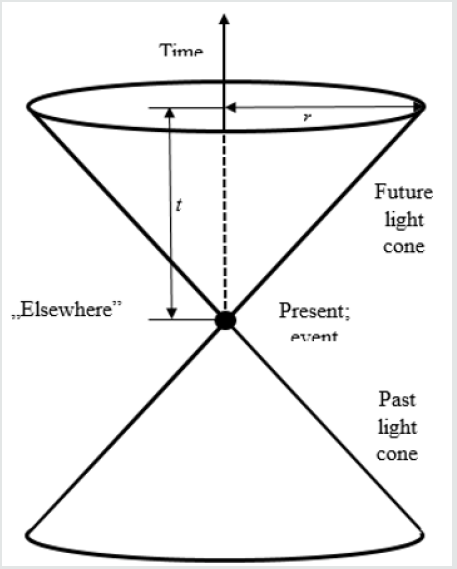
In physics there is known the notion of “light cone” (Figure 1).
It is “a surface in space-time that marks out the possible directions
for light rays passing through a given event” [4]. Let us look closer
at this cone. The basic rule of its construction is the fact that
“nothing can move faster than light” [4]. Therefore, if anything lies
in the distance greater than that, which during observation might
be travelled by light, is located “elsewhere”, i.e., in the space, from
which no information may be received by observer. Accordingly,
such an information cannot influence the run of events in the spacetime
region encompassed by the light cone. And vice-versa. If a given
event starts a cause-effect chain, it may act only inside the light cone
(Figure 1). Therefore, such a representation of reality divides the
whole space-time of events into two parts. Inside the cone, there
are some mutually related cause-effect chains, which shape the run
of events, but the information from outside the cone (“elsewhere”)
cannot influence such a run. On the other hand, the actions inside
the cone have no effect on what is going on outside it. The light
cone is no doubt a mathematical structure. Therefore, according
to earlier statements, it should not be useful in the description of
psychical processes underlying human motor behavior.
Figure 1: The light cone. The events from “elsewhere” cannot influence the events inside the cone. It would be possible only
when the information from this region would be able to travel faster than light. After time “t” from the moment of event, the
light will reach the distance “r” from the place of event.
Anthropokinetics and physics
However, the anthropokinetics is still young discipline,
which searches for its scientific identity. Therefore, it is forced
to adopt what might be termed the “Foraminifera-strategy”. The
Foraminifera are one-cellular organisms, which build around their
bodies the shells of sand. However, they select only such grains
that under microscope their tests look as if they were polished [5].
Anthropokinetics should take any suitable “grains of knowledge”,
no matter, where they come from, either. Accordingly, let us listen
to novelist Jo Nesbø, who wrote: “You can discover new things
by changing your perspective and your location (in science their
equivalent is the methodology-WP). You can compensate for any
blind spots” [6]. Accordingly, let us try to look at anthropokinetics
from slightly different perspective. Already in 19th century
philosopher, Auguste Comte has divided the whole science into two
parts: “physique organique” and “physique inorganique” [7]. The former might be-roughly-identify with the biology, whereas the
latter-with physics. The common element is the “physics”. Hence,
one may perceive it no as a sum, but as a system. In such a situation
justified seems to be the presumption that-may be-some relations
are active in both these regions, but in “physique inorganique” they
are better visible, whereas in “physique organique” are hidden
deeper. In such a context highly illustratively sounds the statement
by Niels Bohr that “It is wrong to think that the task of physics is to
find out how Nature is. Physics concerns what we say about Nature”.
While coming out from such a “starting point”, one might
put a question, whether the physical-mathematical structure of
the light cone (or, more precisely, the philosophy underlying its
mental construction) might be useful also in description of any
psychological processes (in general) and anthropokinetical ones (in
particular)? In other words-whether in anthropokinetics we have
to do with relations independent of an individual, which executes
a motor operation, which are able somehow “from outside”
impose specific constraints on potentialities of performing by this
individual specific motor actions? And whether to description of
such a relation one might-even marginally-use a physical model?
Brain skyscraper and modalities ladder
The questions put above may be answered positively. Such
external (against, e.g., an individual human) system of constraints
is the “brain skyscraper”, shaped by evolution. It has been invented
by Nikolai A. Bernstein [8-10], and its “intellectual daughter” is
the modalities’ ladder [2,3]. The latter is fully coherent with the
“skyscraper”, but devoid of evolutionary and neurophysiological
components; it is mainly information-processing structure. Both
are hierarchic, systemic structures. The former has five levels, the
latter–five rungs. One if the main rules by Bernstein states that
each motor operation has its main level of control (“master”),
where the attention of the executor is being focused, and the
lower ones (“slaves”) play the function of “background” (not
“subconsciousness”, whatever this term might mean) and their
action does not need attention concentration. Let us emphasize:
the main criterion is not a division into “consciousness” and “subconsciousness”,
but into elements, which need attention focusing
and such ones, which do not need such a concentration. Before
comparing the “brain skyscraper” and the modalities’ ladder, let us
remember that one and only manifestation of each mental, psychical
process in living beings-including humans-is the movement. This
is why philosopher Andrzej Wohl wrote: “All that we dispose of,
all what constitutes the resource of our culture, all the pieces of
art, science and technology-all that results from motor activities”
[11]. In short, there are no other conducts than the motor ones.
The basis of such a behavior is the consciousness. Before further
considerations, let us formulate the two definitions:
A. Motor operation: Motor action of a living being aimed at
solving of a given task in environment; it may be evoked either
by extrinsic stimulus (trigger; in such a case it is the motor
response), or by intrinsic motivation without any contact with
environment [12].
B. Consciousness: A dynamically changing component of a
quasi-static whole; the multimodal knowledge of an individual,
activated at given moment by perception directed by attention,
aimed at dealing with a task at hand [3].
Let us add that the consciousness is a multifaceted phenomenon.
Knowledge might be described with various codes-e.g., haptic,
visual or verbal-but the general term “consciousness” encompasses
all these modalities of information processing. It seems worth
remembering that the term “modality” includes a specific code of
information storing and processing, a logic specific to them, certain
scale of phenomena and processes, the definite time period and
depth of information processing. The characteristics of the “brain
skyscraper” and modalities’ ladder, as well as the phenomena
related to them, have been presented in Table 2. In short, the brain
skyscraper has been built on structural, whereas the modalities’
ladder-on functional basis.
Table 2: Bernstein’s “brain skyscraper” and the modalities’ ladder.
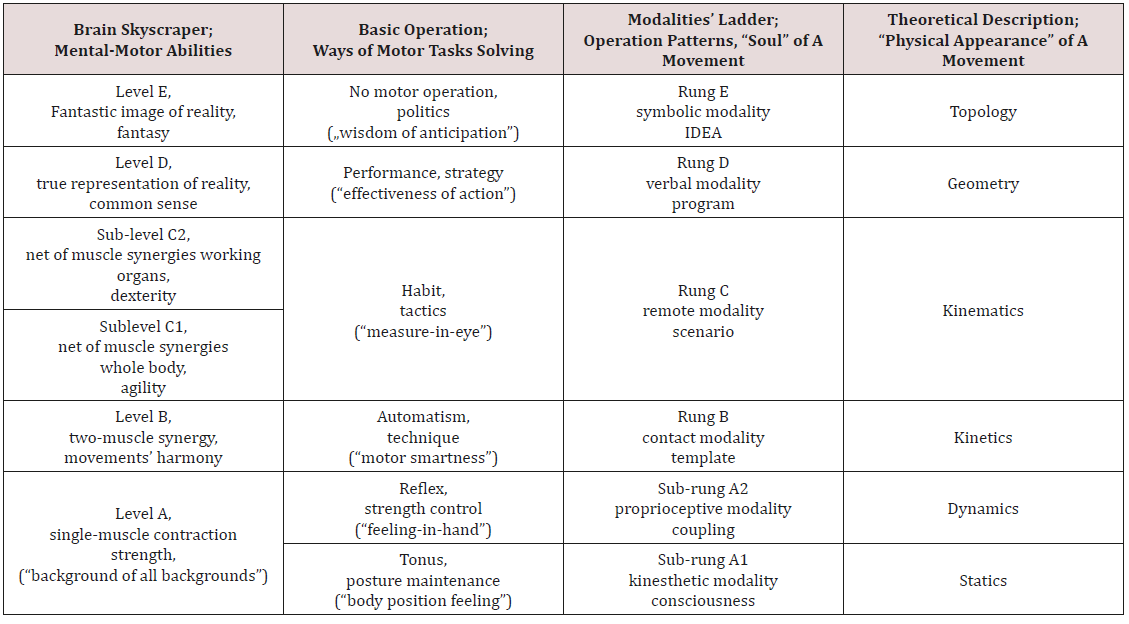
As one can see, the divisions in both these structures are not
identical. The equivalent of the single A-level in “brain skyscraper”
are two sub-rungs (A1 and A2) in the modalities’ ladder. A single
C-rung in the modalities’ ladder has two sub-levels (C1 and C2)
in the brain skyscraper. Some comment needs the function of the
tonus (sub-rung A1) in the structure of any motor operation in a
human. The skeleton of Homo sapiens amounts to about 200 bones.
Each of them may move against other ones; such movements may
be described with the term “degrees of freedom”. In sum, human
skeleton disposes of very many degrees of freedom. However, if a
muscle should to move a given bone lever, then one its end has to be
fixed relatively stiffly. In other words, all bones in a kinematic chain
ending with this “stiffly fixed” end of the muscle should be properly
immobilized; Bernstein dubbed this process “reduction of freedom
degrees”. It makes the main task for the muscle tonus. Thanks to it,
non-controllable system has been transformed into a controllable
one. Hence, the muscle tonus makes a basis for the all other motor
operations. Therefore, Bernstein termed it “background of all
backgrounds”. In the modalities’ ladder, the notion of “degree of
freedom” has been generalized and encompasses the abstract
“information chunks”, related to movements or set of movements,
specific to higher rungs of the modalities’ ladder.
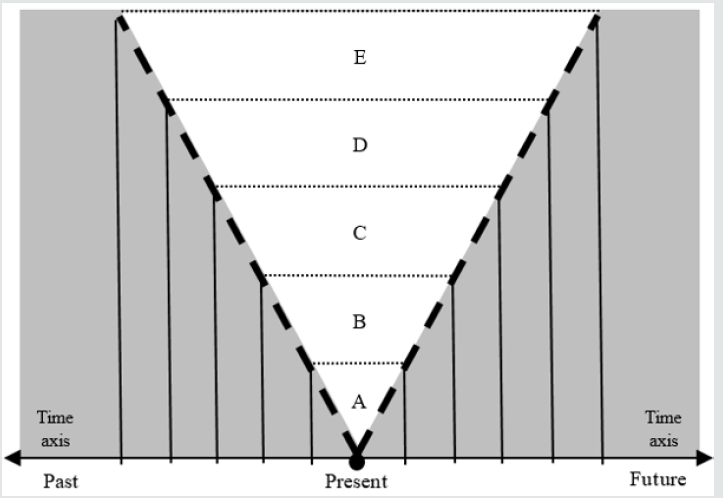
The anthropokinetic events cone
The modality of each rung of the modalities’ ladder includes
a specific type of coding, logics of information processing and
temporal limits of the phenomena under consideration. Therefore,
facing angry grizzly bear somewhere in Alaska, I would prefer
company of experienced trapper with Winchester rather, and not
ingenious Albert Einstein. Just the temporal limits, peculiar to
rungs, may make a structure similar to the physical light cone. Let
us term it “events’ cone” (for the sake of simplicity, because it should
be named “the cone of abstract representation of real events”). A
given modality may effectively “deal” with events, which belong to a
specific period. Hence, the events lying beyond these limits should
be categorized as being “elsewhere” (Figure 1). Consequently, they
cannot influence the information processing inside the events’
cone. It is possible, then, to use the general rule of construction
of the physical light cone, i.e., the division of the space of events
into two parts. One of them includes such events, which may make
parts of cause-effect chain shaping the future, and the other, which
are to be found “elsewhere” and cannot influence the run of events
(Figure 2).
The structure of the light cone differs essentially from that of
events’ cone. In the former the time axis is positioned vertically
(Figure 1), whereas in the latter-horizontally (Figure 2). However,
the general philosophy-division of events and information into
potentially active and unable to any activity-remains the same. It
is worth noting that the time axis in Figure 2 should be perceived
as a logarithmic scale, and not a linear one. Nevertheless, clearly
visible are time periods specific to rungs, and the fact that the
higher the rung, the longer the time period for analysis of events
and information processing (thinking).
As a result, one might consider the space inside the events’ cone
(bold dashed line) makes the room for analyses and information
processing, whereas the space outside the cone represents the
“elsewhere”. In short, the temporal constraints-specific to rungs of
the modalities’ ladder-disable the events from “elsewhere” and make
them ineffective in shaping of a given motor operation. The higher
rung, the longer “working” period. The price, which inevitably must
be paid for its extension, is higher and higher level of abstraction,
i.e., getting further and further from reality. Therefore, the processes
and phenomena at distant to the “tangible” reality highest rungs of
the modalities’ ladder cannot be tested experimentally. Therefore, at
those rungs the only tools for scientific description are hypotheses
and theories. The techniques of intellectual work, which may be
applied in this region of abstraction, are, e.g., the logic of loops
by Michał Heller [13] or “inference to the best explanation” (IBE)
by Gilbert Harman (Harman, 1965). Otherwise, both of them are
nearly identical. Such a “moonshine” way of science creation evokes
almost contempt of “genuine scientists”, i.e., the worshippers of
arithmetical average and standard deviation. Nevertheless, the
science is being composed of theories, and not “new, original
experimental data”. Their amorphous ashes may merely fertilize
the intellectual ground, on which the theories should grow.
This has succinctly expressed by biologist (Nobel Prize winner)
Peter Medawar with the words “theories destroy facts” [14].
Unfortunately, as its physicist Edward Teller aptly stated, “A fact
is a simple statement that everyone believes. It is innocent, unless
found guilty. A hypothesis is a novel suggestion that no one wants
to believe. It is guilty, until found effective.”
However, let us look once more at the Figure 2. Let the symbols
A, B, C, D and E symbolize rungs of the modalities’ ladder, tightly
related to Bernstein’s brain skyscraper levels. The grasping of
time is possible only at C-level-at that level appear remote sensory
organs, which enable observation of motion in the environment; it
is the only phenomenon, which makes possible to shape the notion
of time-but it does not mean that it cannot be used to description
of phenomena also from the lower rungs. The bold dashed line
symbolizes the anthropokinetic events’ cone, including rungs of the
modalities’ ladder. Not without reason the borders between rungs
are marked with the dotted line. In fact, they symbolize not sharp
limits, but fluid zones rather. The information may cross them,
indeed, but in the zone between the rungs, its modality is being
transformed. This is a non-linear process, i.e., elements from one
rung are differently amplified in the other one. This phenomenon
is probably responsive, to the main extent, for unpredictable,
qualitatively new system effect produced by such a system. Let us
notice that such a structure is generally coherent with division of
memory into short-term sensory store (STSS), short-term memory
(STM) and long-term memory (LTM) by Richard Atkinson and
Richard Shiffrin. Roughly, STSS might be associated with the lowest
rungs of the modalities’ ladder, STM-with the middle ones, and LTMwith
the highest rungs. The vertical relations make the system. The
horizontal extension, limited by dashed line, represents the period
specific to the information processing modality at a given rung.
Figure 2: The events’ cone in anthropokinetics. White field inside – consciousness; grey field outside – unconsciousness
(“elsewhere”); bold dashed line – half-consciousness.
Consciousness, half-consciousness and unconsciousness
At that moment of our analyses appears the space for mental
construction of what might be associated with the phenomenon
commonly termed “sub-consciousness”. This term seems to be
incorrect, because it not describes the essence of the phenomenon
under consideration. It may be regarded as a specific “black box”,
where one may put all, what scientists are not able to properly
describe scientifically. In such a situation, the item put into black box
termed “sub-consciousness” remains not understandable, indeed,
but marvelously gains the attribute of “scientificity”. However, one
might imagine that the borders of the events; cone are not sharp as
the cut of Japanese sword, but they make rather some fluid zones.
While approaching the inside of the cone, the image of a given
phenomenon or process becomes more and more pronounced, and
inside the cone are completely clear. In such a model, each of the
rungs-which dispose of its “own” modality of information processing
and temporal limits of abstract representations of phenomena and
processes-has also its own “zone of twilight of perception”. Such
a model would enable description of the phenomenon of gradual
forgetting of a particular event. It would transfer from the inside
of the events’ cone-in this region, its abstract representation is
immediately accessible-to the “twilight zone”. Its retrieving from
this zone is possible indeed, but it is more difficult and time
consuming. Finally, when it goes out from the zone of “twilight”,
it becomes completely forgotten. Such a “twilight zone” from the
side of future one might dub “precognition”, and that from the
side of past- “shadows of oblivion”. The representations of events
in this zone exist, indeed, but they are not precise and indistinct.
Therefore, the interior of the events’ cone may be identified with
the consciousness, the border zone-with half-consciousness, and
the region of “elsewhere”-the unconsciousness.
To avoid creation of a “moonshine” term (like “subconsciousness”),
let us try to invent a rationale for what has been
roughly dubbed “precognition”. Motor operations are always
faced towards future-closer or farther, according to the rung of
the modalities’ ladder. The main “processor”, which produces
the abstract, mental pattern of a motor operation is the intellect.
It may be perceived, roughly as a system consisting of three
mechanisms of information processing: intelligence, intuition,
and instinct. Intelligence makes the “armed forces” of the intellect. It
is responsible for final shape of the motor operation pattern.
However, to produce such a pattern, it needs full information
necessary to given task solution and knowledge of all the rules of
such information processing. We are very rarely in such a luxurious
situation; we have not such a complete knowledge. Hence, if an
information lacks, it must be guessed to get intelligence going. This
makes the task for intuition. Finally, the instinct directs the
searching
for lacking information towards these regions of memory, where
its finding seems to be most probable. The half-consciousness zone
faced towards future cannot include the full information about a
given task; otherwise, it would be the full consciousness. Hence, the
intelligence itself cannot be effective in this region. As a result,
here
opens the wide field of action for intuition. The term “precognition”
might be described, then, as a way of processing of not complete
information, where the main tool is the intuition (“I don’t know, but
I suppose”), and only marginal role plays the intelligence.
The Events’ cone in practice
The system presented in the Figure 2 may make sense only when
the time period, assigned to a given rung, is sufficiently long to enable
practical realization of the task related to this rung. Therefore, the
lower rung, the simpler operation and the swifter its execution. And
vice-versa: the higher rung, the more time-consuming preparation
and execution of a specific motor operation. Let us imagine such a
situation. During a solemn, international scientific conference, I am
presenting my work. I am moving freely in the room and using a
pilot for changing slides remotely. Suddenly, I take a pin, hidden in
my sleeve, and acutely sting the buttock of a dignified, gray-haired
scientist. What will happen? No doubt, the scientist will jump. It
is natural reaction in such a situation: to take a distance from the
source of pain. Does s/he realize immediately, what happened? For
sure-not! Such an event would be so astonishing, so improbable,
without any equivalents in the past, to which it might be related. The
scientist would have to build the abstract model of the event, what
inevitably must be time-consuming. Hence, at the contact B-rung
the stimulus is received, response-prepared and executed, before
at the verbal D-rung the stimulus is barely identified. However, if it
happens, I would be far away.
The content of events’ cone depends not only on information
processing modality, but also on the level of pre-preparation of a
needed operation pattern. In this respect instructively sound the
words by Ben Johnson-mysterious racing driver “Stig” from the
BBC program “Top Gear”. In the interview, he stated: What defines
a good driver? What attribute is necessary, and what merely
useful? The anticipation. Racing driver is a person, who does not
look for solutions of the problems that occur in a race. S/he knows
those solutions, and when the situation comes, when the reaction
becomes necessary, s/he simply performs the operations leading
to its successful solving [15]. While seen from the perspective of
the modalities’ ladder, in this case we have to do with the D-rung
depth of information processing being “pushed down” to the C-rung
temporal constraints. In daily language, such a process may be
identified with what is commonly termed “experience”. It has been
described by Nikolai A. Bernstein [10,16].
On the other hand, if an individual has to his/her disposition
C-rung time, one cannot expect the information processing with
depth specific to D-rung. In such a situation suitable information
processing should be located in the region of “elsewhere”. For
example, the analysis of car accident or ships’ collision at sea,
where the teams of expert witnesses have plenty of time for D-rung
calculations and analyses, cannot be compared to the situation of a
driver or captain, who was able to make only C-rung assessments,
basing on previous experience, and had to his/her disposal merely
seconds or minutes. Such a situation has been brilliantly presented
in the movie by Clint Eastwood “Sully”, about landing on 15th
January 2009 on the Hudson River of the Airbus 320, in charge of
the captain Chesley “Sully” Sullenberger.
Conclusion
Well, is it possible-based on the presented analyses-to formulate
the conclusion that the laws of physics in their “pure” form may be
applied also in anthropokinetics? For sure-no! One might merely
assume that some mental structures, invented by physicists, may
be used-after specific modifications-also in anthropokinetics.
However, such an analogy reminds the similarity of the shark and
the dolphin rather, and not a common law being in force in both
these disciplines. It is not possible, then, to perceive it as a rule.
In science there are no any well-worn, simple templates-like, e.g.,
calculations (not mathematics!) or any other commonly accepted
methodologies”-which would release scientists from thinking. In
this respect highly instructively sound the words by Niels Bohr:
“You are not thinking; you are just being logical.”
Philosopher Paul Feyerabend has invented an image of
knowledge built by Truth and Freedom. The former has its feet
firmly on the ground; the latter flies freely in the sky. Where they
meet, the Science (with great “S”) is being born. However, the Truth
is harnessed with the stiff constraints; hence, it cannot for long
remain in union with the unhampered Freedom. Hence, sooner or
later, they must part their ways. Until next meeting. Analogously,
also the similarity of the light cone and the events’ cone should be
treated as a result of a momentary meeting of the Feyerabend’s
Truth and Freedom, and not as a basis for formulation of more
general theories.
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Medical Sciences Please Click on the below link :
https://lupine-publishers-medical-sciences.blogspot.com/