Lupine Publishers | Archives of Nanomedicine: Open Access Journal
Introduction
Over the last years, nanotechnology has been introduced in our daily
life. Nanotechnology may be able to part in a very range of
applications, such as in nanomedicine, nanoelectronics, biomaterials
energy production, and consumer product, etc. The application of
nanotechnology for medical purposes has been termed nanomedicine and is
defined as nanoscale tools (e.g., 1–1000 nm sized) for the diagnosis,
prevention, and treatment of diseases. The term nanomedicine appeared in
the 1990s, and since then, has the potential to significantly improve
some current treatments. Commonly, nanomedicines consist of active
pharmaceutical ingredients such as small molecules or biologics packaged
into nano-sized carriers made of excipients like lipids and polymers.
By packaging drug in the particles, drug concentration in the target is
maximize by passive or active targeting and
pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamics profiles are improved. But due to their
size related physicochemical properties, nanomaterials can require
additional quality and safety testing compared to products with standard
size.
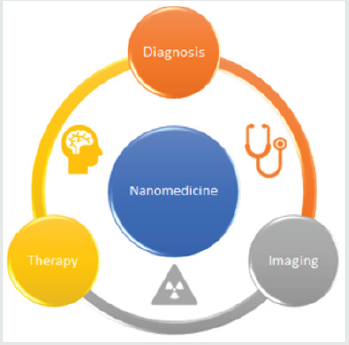
In nanomedicine, nanomedical devices can be used for analytical,
imaging, detection, diagnostic and therapeutic purposes and procedures,
such as targeted cancer therapy, drug and gene delivery, improving
cell-material interactions, scaffolds for tissue engineering, etc. The
application areas of nanomedicine are shown in Figure 1.
With the developing technology and increasing life expectancy, new
problems are faced in human life. Science is actively working to offer
solutions to these problems. The advancing technology and increasing
knowledge, the reliability of the products and techniques used for
years, started to be questioned and the problems identified led to the
development of new solutions. Over than 160 years, dentistry has been
used silver amalgam for tooth filling material which contains
approximately 50% Hg metal. During the past decay, science demonstrated
the released Hg from
the filling material covalently bound to cell proteins and shows
toxic effect. So, the presence of toxic and trace elements in dental
powders has led to the discover better dental filling materials and
tests. In this context, Joseph published a research article about Al
detection in dental powder by using handheld X-Ray Fluorescence (HHXRF)
(Joseph, 2019). On the contrary of conventional XRF, HHXRF has an
advantage of showing Al which is a prominent element in dental powders.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is one of the most common and
deadliest infection for many years. During past decades, many efforts
have been made to reduce the level of the diseases. Gupta et al.
reviewed the mycobacteriophage to control tuberculosis infection (Gupta
et al., 2019). Mycobacteriophages are the member of a group of
bacteriophages that infects Mycobacterium and have two killing
mechanisms such as lytic and lysogenic. Endolysin and lysB proteins have
a major role to disrupt cell wall envelope of the bacterium.
Mycobacteriophage therapy is a novel study for Tuberculosis which is a
common and deadliest infection disease.
Both in nuclear and thermonuclear power engineering, hydrogen
could be the first reason of equipment damage. Because of that,
reactor pressure vessels (RPV) was manufactured without stainless
cladding as a product of RPV wall corrosion. In the RPV steel,
hydrogen concentration was determined with gas chromatography.
The hydrogen content in the irradiated steel were found less than
0,1 ppm. This was attributed to the increase in hydrogen content as
fast neutron fluency increased (Krasikov, 2019).
“If one day, my words are against science, choose science”
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
Read more about Lupine Publishers Archives of Nanomedicine: Open Access Journal Click on the below link: https://lupine-publishers-nano-science.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.