Lupine Publishers| Journal of Cardiology Research & Reports
Abstract
Background: Real-time three dimensional transesophageal echocardiography or RT-3DTEE, with advances in image processing and display, has increased the availability and utility of TEE to a variety of clinical settings as diagnosis and catheter intervention.
Patients & Methods: We study all Patients with RT-3DTEE, presented in MEDIC HCMC from October 2010 to May 2020.
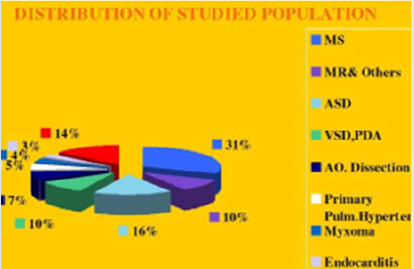
Results: From October 2010 to May 2020, in MEDIC HCM, we have already performed 1276 cases ofReal-time 3DTEE: Mitral Stenosis (31%), Atrial Septal Defects (16%) and other diseases of the heart.The display of three dimensional images of 3DTEE providing important information’s to assess the anatomical structures and the severity of diseases prior to perform interventional procedure.
Conclusion: Real-time 3DTEE overcomes the limitations of 2DTEE in making diagnosis and guiding the catheter intervention.
Keywords: Three Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography; Mitral Stenosis; Atrial Septal Defect
Background
The first utilization of a TEE device that promised to have clinical utility was reported in 1976 by Frazin and coworkers, who described the application of transesophageal M-mode echocardiography. The use of this technology was subsequently reported for the evaluation of ventricular function during supine exercise. The next success was the development of real-time, twodimensional TEE imaging, as first described in 1980 by Hisanaga, who developed a wide-angle mechanical sector scanner, while in 1982 Schluter reported on the use of transesophageal phased-array two-dimensional echocardiography. The incorporation of color mapping into a TEE device was first reported by investigators from Saitama Medical School in Japan. The same group was instrumental in early development of standard biplane, matrix phased -array biplane, and small pediatric probe. The current-generation probes are all multiplane devices. Rotating the small control wheel flexes, the tip to the left or to the right. But with the multiplane TEE transducer, this manipulation is rarely necessary. Rotation of the transducer refers to movement of the sector scan from 0 to 180 degrees. Transthoracic and transesophageal real-time three dimensional echocardiography is a significant advancement in technology. Advances in image processing and display, the addition of three dimensional imaging capability, and the portability of ultrasound system have increased the availability and utility of TEE to a variety of clinical settings as diagnosis, cardiac catheterization, operation and intensive care. Currently percutaneous interventions for many structural diseases increase more and more in our country. Interventional cardiologists are now treating a variety of lesions that previously required surgery as mitral stenosis, aortic stenosis, ostium secundum ASD, VSD, PDA, Coronary Fistula… Although Fluoroscopy and 2D TEE are usually used for procedural guidance, real-time three-dimensional TEE offers several important advantages over these modalities. Previously, Toshiba SSH 140 A with TEE biplan probe have been used to perform 2D TEE in our hospital. Since October 2010, transesophageal echocardiographies are made by X-MATRIX, iE 33 Philips machine.
Endpoints of study
i. Role of 3DTEE in the assessment of heart diseases.
ii. Advantages of 3DTEE in compare with 2DTEE.
Patients and Methods
a) Pts with 3D TEE at MEDIC HCM, Viet Nam, from October 2010 to May 2020.
Instruments: X-MATRIX Philips iE33, X-7 real-time 3D TEE probe.
Acquision mode including Live 3D or narrow sector, Full Volume or wide sector, Zoom or the smallest pyramydal size available for acquisition.
Techniques
i. Explain the procedure to the patient.
ii. The patient should not have had any intake of food or drink for at least 4-6 hours.
iii. Oral prostheses should be removed.
iv. The patient should be placed in the left lateral decubitus position.
v. Topical anesthetic and sedation.
vi. Introduce a bite block between the teeth.
vii. The probe is gently passed into the oral cavity over the tongue and guided into the larynx.
viii. The patient should be asked to swallow, the probe is gently introduced into esophagus.
b) Case series report study is applied for this topic.
c) The advantages of 3DTEE in compare with 2DTEE in diagnosis and evaluation of diseases prior to perform interventions.
Results
From October 2010 to May 2020, in MEDIC HCMC, we have already performed 1278 cases of 3DTEE: Mitral stenosis (31%) and other valvulopathie including Mitral Regurgitation, Aortic valvopathies, Atral Septal Defects (16%) and other shunts as PDA, VSD; then Myxoma and cardiac tumors, Endocarditis, studying prosthetic valves. The other complicated cardiopathies as Coronary artery fistula, Valsalva sinus rupture, Ebstein anomaly. The percutaneous balloon mitral valvuloplasty, transcatheter closure of ASD and surgery have demonstrated the precised diagnosis of 3DTEE (Figure 1).
Among 396 Pts with MS, mean age=45 (from 18-72 ages), the majority of patients were female (75,2%), Dyspnea is the first symptom to the consultation, sometime embolic events (7.5%) keep patients going to their cosultants, AF account 6,1%. Rheumatic Fever is predominant cause, with important fusion of commissures (70%), 2DTEE completed by 3DTEE is used to calculate the Wilkins score, providing information’s more exactly than 2D TTE alone, prior to perform Balloon Mitral Commissurotomy or surgery. MVA3D measured by Real-Time 3DTEE to compare with conventional two-dimensional planimetry MVA2D.The 3D Assessment was significantly smaller the 2D planimetry: MVA3D=0.95cm2±0.21; MVA2D=1.16cm2±0.24; mean difference=-0.21cm2, n=327, p<0,001. Some patients with high Wilkins score evaluated by 2DTEE still have responded well to Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty. Real-time three dimensional transesophageal echocardiography provides important information’s regarding the involvement of rheumatic process on the mitral valve, particularly the symmetry length of commissural fusion. Furthermore RT-3DTEE also shows the thickening, the fibrosis and the calcification of the whole mitral commissures that cannot be visualized by 2DTEE. The 3D image allows superior visualization of the thickening of the mitral leaflet, particularly the commissures. The 3DTEE usually details the sub valvular apparatus not appreciated on 2DTEE while studying the leaflets. Because patients often presented late in Hospitals, their Wilkins score usually is high (68% with Wilkins score is superior to 8). Especially, LAA thrombus, even small size, furthermore, can be detected more clearly on RT- 3DTEE. Volume and mobility of LAA thrombus appreciated better on 3DTEE. Detection LA and LAA thrombus by RT-3DTEE is more sensitive than 2DTEE with X-plane mode and 3 D Zoom only are available in 3DTEE. Direct planimetry of mitral valve orifice by 3DTEE is the gold standard method now. The cropping function ensures that the orifice area is traced in a plan that is at the tip of the mitral valve (Figure 2-17).
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Cardiology Research & Reports Please Click on below Link: https://lupine-publishers-cardiovascular.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.