Lupine Publishers | Journal of Textile and Fashion Designing
Abstract
Keywords: Wearable technology; Thermal protection; Conductive textile; Silver-coated yarn
Introduction
Meanwhile, although human can survive through the low temperature condition, thermal comfort is still a problem that the traditional passive thermal-insulate clothing protection, which is thick and in blocky multi-layer structure, to prevent the heat dissipation to the environment as less as possible. In this circumstance, the heat energy source is only the human body itself. While in these extreme condition, the tradition passive thermal protection is insufficient. Further, this bulky and massive multilayer structure constrains the free movement of human beings, especially when human doing exercises and conducting works in chill winter outside trials.
Typically, the applicators involve relatively thick bulky compresses which do not conform closely to the contour of the body. Failure of the compress to conform closely and to retain close contact once positioned, results in irregular heating of the ski area. This problem often results in irregular or non-uniform healing of the skin, swelling, and the like. Further, due to its passive working-machinimas, this protection is far insufficient to maintain the thermal comfort of wearers in extreme condition, especially for the children and the elderly groups. Thus, an innovative flexural wearable active thermal technology is under research [1-3].
On the other hand, wearable smart textile is a new technology emerged two decades ago. After 20-year continuous developing, this technology already expends its applications into different fields, such as fashion, home textile, medicine, sports, military etc. It integrates flexible conductive materials to form complete electric circuit or functional e-components and connected to external circuit to achieve designed responsive functions towards outside stimulus or to enlarge the human themselves capability to against outside the environment. Currently, textiles are transcending their traditional functions and embrace various new possibilities to fulfill new roles in innovative functional exploration. Fibers are dramatically transforming the world and environment around.com and as they do so, they are also inspiring radical new visions for the future.
In this way, thanks to the fast-growing wearable smart textile technology, conductive textiles with various electric resistant properties, can be applied for developing the proposed light, flexible active thermal-protective clothing products, through different fabricating methodologies to integrate these conductive textile materials together with different areas with different electric resistances so that following the Joule’s law, the target positions in a conductive fabric will enable to heat up actively when certain electric energy provided. This active thermal textile can be widely applied in the fields of professional and protective thermal wear, fashion, sport and well-being, home interiors, automotive, construction, medical and health care etc. Especially the fields, sports and medicine, are the two main drivers for further growth, because the attitude shift of our main consumption power that everybody is towards to pursuing for a healthy life manner, and the social aging problem is becoming more and more severe, the market potential is unpredictable [4-7].
The Thermal-protection in Various Scenarios
Scenario I-Thermal Treatment
Thermal treatment, or the manipulation of body or tissue temperature for the treatment of disease, can be traced back to the earliest practice of medicine. Cultures from around the world can point to ancient uses of hot therapy for specific medical applications, even including cancer. Today there are a growing number of clinical applications of thermal therapy that benefit patients with pain-relief, a variety of diseases and heat-activated drug delivery. In order to deliver a better therapy effects in a constant period, the thermal functional textile is required to closely fit with the body curve and contact the target skin position with large area and distribute the heat energy evenly in case any overheating occurs. Further, this technology can be extended to other fields, to offer this treatment all the time. It can integrate with fashion and textile, transportation and home textile, such as smart thermal mattress, sheets, pillowcases etc. to offer an active thermal comfort or thermal treatment to achieve better fatiguerelief and pain-relief effects. Especially, in the scene of home textile, through this next-to-skin technology, electric energy consumption can be significantly saved, compared to the traditional air-condition controlling manner [8-12].Scenario II-Chilling Sports Field
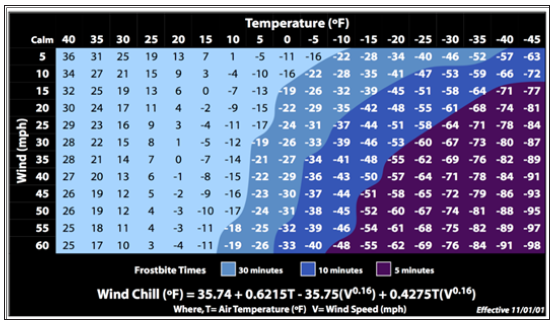
Driven by the public pursuit for a healthy modern lifestyle and a perfect body figure, an upsurge of physical training and fitness is sweeping the entire world that everyone, not only professional athletes anymore, is taking exercise all the year around, even in the chill winter outside fields. This trend also boosts the consumption of thermal-protective sportswear recently. When the environmental temperature drops below 5ºC, it is already dangerous to conduct outdoor exercises that cold injuries may occur, especially when taking wind this factor into consideration. The relationship among the health risk, the tense of wind, the environmental temperature and the time of human subject exposure in the outdoor, is well studied and listed in the Figure 1. It shows that in the condition where the temperature under 40°F (5 °C) and the wind intense than 5mph/h, and the exposure time exceeds 30 min, there is a high risk to get cold injuries [13,14].
Figure 1: Wind Chill Temperature Index in Fahrenheit [14].* Wind Chill Temperature is only defined for temperatures at
or below 50°F and wind speeds above 3 mph. Assumes no impact from the sun, i.e., clear night sky. Frostbite times are for
exposed facial skin.
Thus, sufficient thermal protection against the chill condition
is critical both for elite athletes and common sports consumers.
For elite athletes, injuries may lead to missing the whole season,
which also means losing sponsor deals and possible prize money.
For common sports consumers, injuries may cause, for example,
sick leaves from work, monetary losses both for the society and
the individual. Injuries can also cause mental problems, especially
for elite athletes, whose career depends on their bodies and its functioning. Injuries also may harm the physical progress,
especially on young athletes, who develop quickly and might fall
behind because of the cold injuries [15].
However, facing this high injury risk, the only current solution is to wear multi layers of clothing, which is heavy and blocky in the end. The cumbersome and multilayer-structure cloth of such clothing restricts physical motions and normal consumers will feel more exhausted, which makes it impractical. It is critical that designers understand the movement needs of individuals who will wear these thermal protections. Movement involves time, energy and space. Among these three elements, they need to rank after their importance by gathering realistic information from the practices. Additionally, it is suggested to take off the out layer after excises and starting to sweat out. However, how to deal with the taken-off clothing will be a problem. Carry them around and do strenuous exercises simultaneously? Of course, it is a distraction from the exercises. Therefore, the proposed wearable thermal textile can act as the second layer of sports skin to against the chill weather intelligently [14].
Scenario III-Freezing Working Condition
Anyone working in a cold environment is at risk of cold stress. Some workers may be required to work outdoors in cold environments for extended periods, for example, snow clean-up crews, sanitation workers, police officers and emergency response and recovery personnel, l emergency medical technicians etc. The most relevant cold-related health problem was episodic finger symptoms (50%), followed by respiratory symptoms (21%), peripheral circulation symptoms (20%), and repeated pain in the musculoskeletal system (12%). Thus, in order to protect the life-safety, to prevent cold injuries and offer better welfare and protection, active wearable thermal-protective working uniform needs to be developed as soon as possible to lower the risk of cold injury. Besides these three scenarios, there are also other various situations. For example, in the fall-winter collection design of fashion clothing, flexible wearable and active-thermal textile technology can be applied, with a substantial market share [16,17].The advantages of integrating textile and engineering
On one hand, this wearable electric thermal technology is an integration of both textile and electric engineering. Clothing is physically proximal (close to the body), is socially ubiquitous (worn almost all the time, in almost all situation), and has a large contact surface area with the human body. And it can better fit body curves so that, for the technology, the proposed electric thermal-functional device can more closely fit the body with more space offered for free motions, more evenly heating up the subject with less weight burdened simultaneously. These characteristics enable the proposed technology more friendly to wearers in more situations and to integrate more seamlessly into everyday or job-related activities [18,19].On the other hand, electronic engineering offers another significant advantage-the ability to make a change (activated by the user) or response to external stimuli. This proposed wearable thermal technology can adjust its heating effect to against the changing outside condition and maintain in a stable thermal comfort for wearers. Thus, this active thermal functional clothing act as an intelligent barrier between the wearer and the hazard condition. Further, thanks to the clothing and textile property, the electric thermal function area and circuit connecting path can be arranged into fabric pattern design within different structures, consequently, with various surface resistance properties. Following the Joule’s law, multiple levels of heating effect can be achieved. When investigating the technology deeper, this thermal-functional textile can offer the listed detailed advantages:
a. Clothing embedded electrodes enable perfect electrode placement and shape with larger contact area, together with the textile flexibility property, guarantee the electrodes to have a proper skin contact to perform stably.
b. Cables and wires can be integrated into textile invisibly and the system invisibility makes it acceptable for more users.
c. The comfortability and softness of electrodes enable long time wearing, without a compromise of comfort.
Figure 2: The integration of textile and thermal engineering into one wearable electric thermal product.
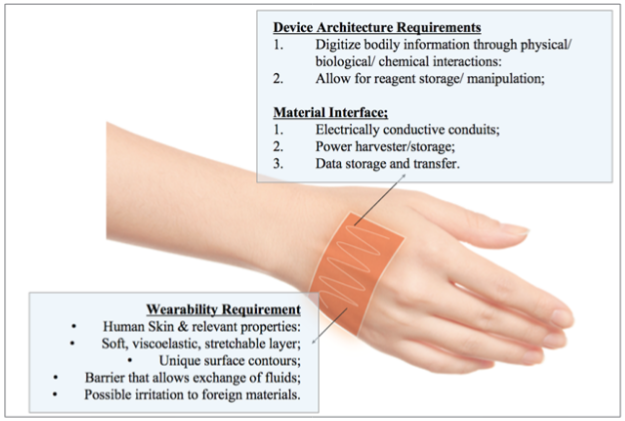
d. Artificial intelligent technology may further enable
this thermal-functional fabric to collect physical/biological/
chemical signals from the wearers and allow for reagent
storage/manipulation, such as a storing encapsulated medicine
inside and paired with the electric heating ability, a better
thermal treatment effect can be achieved. As shown in Figure 2,
the further expectation about the product has been described
in details.
Figure 3: The product development route
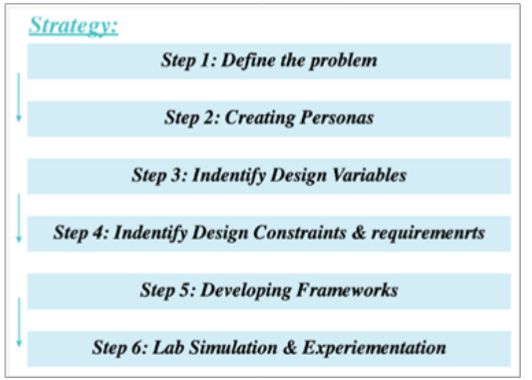

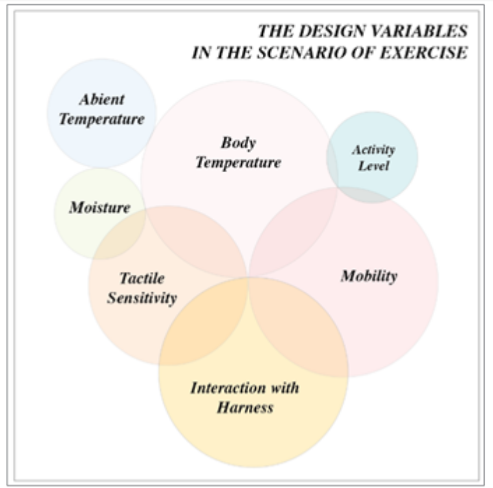
Figure 4: Product design variables in the scenario of doing exercises.
Wearable conductive textiles have been under development for
decades, however, there are rare commercialized products on shelf
and no transfer from this technology into final products in the three
most common scenarios or etc. There is still a huge barrier between
the lab-achievement or trials to commercialized products. A
systematic technology developing methodology system (as shown
in Figures 3 & 4) should be established to broad its applications
and facilitate the transfer from lab-research outcome to the mass
production and realize its commercial value.
Considering the three most common scenarios as the application background, the first step is always to precisely define the problem. Before coming up with the solution, the question that who is the real user and who is the decision-making consumers, should be answered at first with a full consideration even about their different pursuits on a same product, especially when creating different personas and associated with their customized design variables, constrains, and requirements. With these details settle down, they can be organized into a comprehensive framework to conduct the development and in the lab simulation & experimentation step, the performance of the prototype technology can be evaluated and be improved further.
Here, take Scenario II as an example to illustrate its developing methodology. First, the pain point is the insufficient thermal protection or the current thermal protection technology is blocky, heavy, inconvenient for athletes to do exercises or race in the cold condition, perform unsatisfied and easy to get cold injuries. The target personas can be both amateurs and professional athletes, who will be exposed to outside chill weather to do exercises for an extended period. Afterwards, when brain storming the design plan, numerous factors need be considered. Here, 4 main factors will influence the wearer’s thermal balance and comfort: the original body temperature, the ambient temperature, the activity level, the amount of perspiration (moisture), in the thermal convection and conduction these two ways. Additionally, factors, such as mobility, interaction with harness, tactile sensitivity etc., will influence the wearing comfort, especially for doing exercises, the freedom to do different motions is as important as the thermal-protection. Thus, these factors have the same weight in the design plan. In order to meet the requirement of light, flexible, thin conductive fabric with different parts with different electric surface resistances, which can fit tightly with the body curve as well, appropriate conductive textile materials should be sourced for further product development.
Conductive Material Selection
Electronic textiles rely heavily on fiber function and properties to create structures with specific architecture, functions and properties. Nowadays, advancing technical fibers are designed to be electrically conductive, lightweight, flexible and strong. Especially, metal such as silver, copper and nickel can be combined with technical fibers to create flexible, wearable substrates that conduct electrical signals, response to external stimuli and be electric-thermal active.Answering the aforementioned product expectation, various conductive fibers (conductive modification made in the fiber-level) are sourced, they mainly include:
i. Metal/metal oxide fibers/yarns produced by wire drawing,
ii. Conductive synthetic fiber/yarn and through melt spinning and incorporating conductive fillers
iii. Treated coated conductive fibers
iv. Carbon black, metal wires, graphite and metal powder or flakes of Al, Cu, Ni, Ag). However, carbon fiber is likely to shatter when impacted and bristle, uncomforted to wear so it is not discussed here [19].
i. Metal/metal oxide fibers/yarns: The fibers through drawing die, usually consists of a steel mount with a core out of ceramics, carbide or diamond. The initial diameter of the metal wire varies depending on the material. Metal fibers are strength, stable composition, biological inertness and ready availability in textile form at low costs. Due to its inertness, it is not sensitive to washing or sweating. However, they cannot provide uniform heating and their brittle characteristics can damage spinning machinery over time. Additionally, they are heavier than most textile fibers making homogeneous blends difficult to produce. Therefore, based on the technology of conductive fiber/yarn, they are integrated into the textile production and construction and connection development to overcome the barriers. Meanwhile, the conductive metal fibers could be spun with non-conductive fibers to form blending conductive threads to integrate the advantages of metal fibers and traditional fibers, like cotton and polyester together.
ii. Conductive fiber through melt spinning and incorporating conductive fillers: As the two methods shown in Figure 5, one way is adding electric conductive particles into fibers polymer to achieve conductive raw material chips to spine conductive fibers/filament afterwards. The other method is to modifying the polymer property, such as chemical oxidative polymerization, to enable the synthetic fiber conductive itself. Comparing the conductivity of these two kinds, the former one mainly depends on the wt. % of conductive particles added, while the second one’s resistance is relatively high. Meanwhile, this approach could be applied in the field of filament, bio-component fiber productions and piston spinning plant. These conductive particles could be carbon black, graphite, metal powder or flakes of Al, Cu, Ni, Ag etc. [20].
Figure 5: The conductivity modification at the fiber-level
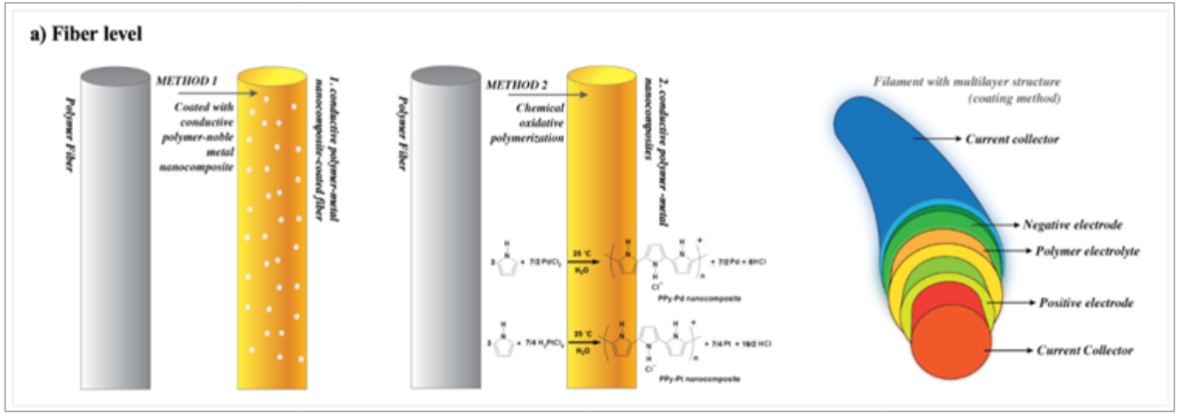
iii. Coated Conductive Fiber: A layer of conductive substrate
is coated onto the non-conductive fibers/filament. The advantage
of coatings is that they are suitable for many fibers types and they
produce good conductivity without significantly altering existing
key substrate properties such as density, flexibility and handle. It
is possible to make a conductive fabric through a coating treatment
even though the main applications for these textiles are protection
against static electricity charge and electromagnetic interference
(EMI). The main advantage is that the textile properties of the yarns
are preserved, particularly they remain flexible. Further, due to
various coating materials and different adding wt.% of conductive
particles in the coating layer, fiber or filament resistance may differ
a lot.
Further, among various coating materials, silver particle coated layer exhibits excellent stable electric conductive property. This material enables the conductive thermal fabric lighter, softer, more flexible and elastic, which can tightly fit the body curve, evenly distribute the loaded pressure and distort and swing in large angles with various body movements. Further, through adding different wt.% of silver particles into the coating layer and binding different lines of coated fiber or filament, silver-coated conductive yarn (SCCY) products with different linear electric conductivities can be produced. Further, this kind of conductive yarn can withstand 20 times of washing and maintain stable conductivity at the same time. Therefore, through utilizing SCCYs with different resistances and embedding them into the proposed electric-thermal fabrics, fabrics with various resistance can be fabricated.
Following the Joule’s law, with certain voltage provided, fabrics with different resistances can achieve different thermal effects. Here, synthetic yarns in various morphologies coated with silver layer in different manners are shown in Figure 6, which show 3 main kinds:
a) Single conductive filament, of which with silver coated on synthetic fibers
b) Conductive yarn formed by conductive filaments blended
c) Conductive yarns formed by conductive and nonconductive filaments blended.
Additionally, through multilayer coated (blended with nonconductive and conductive, layer by layer), capacity and energy generator can even be developed, as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Different forms of conductive fiber/yarns:
a) Single conductive filament, of which with silver coated on polyester
b) Conductive yarns formed by conductive filaments blended
c) Conductive yarns formed by conductive and non-conductive filaments blended.
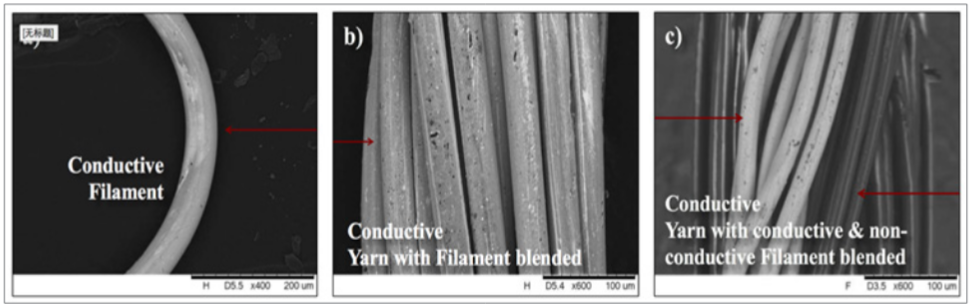

Spinning Methodology for Conductive Yarn Formation
Thanks to the fineness of previous conductive fibers, especially the silver-coated conductive fibers, various conductive yarns (modified in the yarn-level) can be formed, as shown in the Figure 7. Through different spinning methodologies, mainly four kinds of conductive yarns can be formed:a. Blending of conductive & non-conductive fibers, different blending ratio determines the yarn linear resistance
b. Blending of different conductive fibers: different blending ratio and different conductive material selection both determine the yarn linear resistance
c. Core-spun yarn 1, with conductive filaments in the core, and non-conductive fiber wrapped outside to protect the core
d. Core-spun yarn 2: with conductive fibers wrapped outside and the non-conductive filament/ yarn in the core. For these two kinds of core-spun yarn, especially when elastic fiber (such as spandex) combined with conductive fiber/yarn, the elasticity, flexibility and the strength of the proposed conductive yarns are greatly improved, to meet the previous mentioned thermal textile product expectation and enable it to be applied into various scenarios.
Fabrication Methodology for the Thermal Fabric
As previous mentioned, thermal-protective textile needs to arrange conductive yarns or materials in different parts of a fabric with different surface resistance, various fabricating methodologies can organize conductive yarns in different arrangement, in different kinds of integrations, along different directions to achieve different contact resistances. This contact resistance combines, with the linear resistance of conductive yarns themselves, forms the final comprehensive surface resistance. Conductive fabrics can be made by weaving or knitting a fabric entirely out of conductive yarn, by weaving or knitting insulated or no insulated conductors into a standard fabric, or by stitching conductors on the surface of a fabric.
Figure 7: The conductivity modification at the yarn-level
Considering other possible fabricating technologies, the
techniques feasible to conduct electricity using a textile can be
achieved by weaving, knitting, laminating, printing, or stitching
conductive material into or onto the textile structure in general.
While, he most challenge of creating a textile-integrated circuit
is making conductive pathways that can connect components in
different places on the textile. Standard textile structures such as
weaving and knitting usually allow thermal pattern or conductive
yarns to be integrated in a horizontal or vertical direction (or
both) to form electric connecting path or thermal pattern, creating
a grid of functional circuit once textiles are made into garments.
Considering this character, wideness of different fabricating
producing technology adopted and the further feasibility to promote
the proposed technology, three main methods are discussed here:
weaving, knitting and stitch/ embroidery, and together with their
working principle, strength and weakness. Table 1 lists out how
conductive yarns are integrated and Figure 8 illustrates out the
format.
Figure 8: The conductivity fabrication at the fabric-level through different technologies.
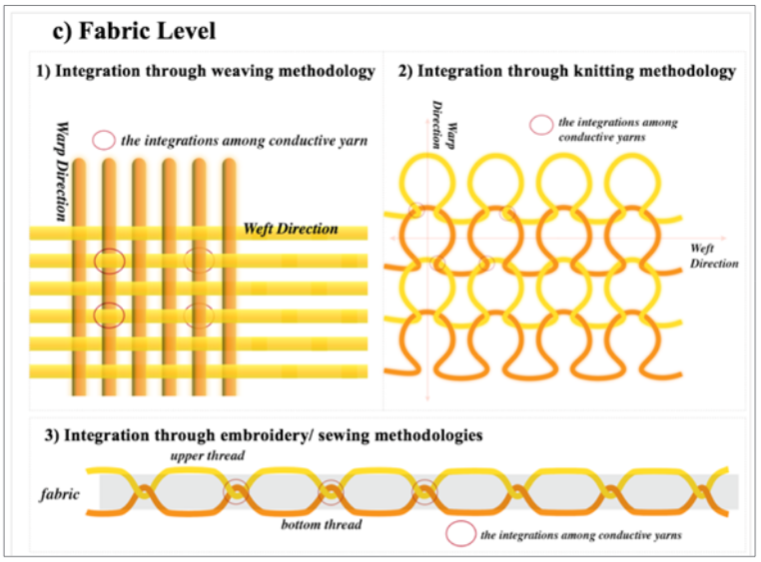

Table 1: The characters of the conductive pattern fabricated through different methodology.
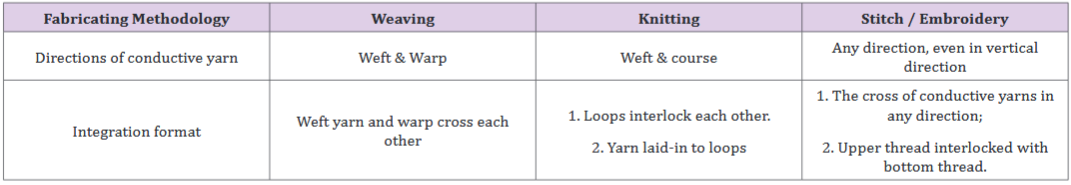
I. Weaving: Weaving is an ancient technique that creates a
simple and effective system today and continues to be at the forefront
of materials innovation. In the weaving structure, the conductive
warp and weft yarns can integrate with each other through square
crossing. Meanwhile, the ordinary weft and warp yarns can be
replaced by conductive yarns to form cross integrations among
them and improve electric conductivity. Through weaving, the fabric
stability quality is excellent and through various jacquard pattern
design, multiple layers can be formed as well. And the warp & welt
yarns can replace the original ones directly. Besides the pattern
design, various conductive yarns can be arranged in specific area
so that even following the same pattern structure, different part
with different resistance can be formed and to achieve a complete
functional electric thermal circuit further. However, in order to
form the cross integration of conductive yarns both in the warp and
weft directions, warp beam composed of conductive yarns need
to form ahead. Meanwhile, for different weaving pattern, different
warp beams need to be produced customized, which costs lots of
time and raw material investment.
II. Knitting: In the knitting structure, conductive yarns can integrate with themselves in the former parts through loop interlocks or the conductive yarn can integrate with other conductive yarns, which are laid into their loops. Knitting fabric structure is more elastic, flexible and light-weight, which can be widely applied in the sportswear design and development. However, everything has its two sides. When the proposed conductive thermal fabric bearing different levels of external extension force, the loops will deform in different levels as well. Thus, the contact morphology between each loop will deform in different level as well, so that their resistance may fluctuate. Depending on specific application scenarios, whether this resistance fluctuation is acceptable or needs to be calibrated should be well studied in advance. However, compared to weaving, knitting production is more fast-response and the design pattern is more flexible to revise with less cost generated.
III. Stitch & embroidery: Stitching or embroidery to the surface of a textile allows for the pathway to be laid out in a more free-form fashion: the yarns can travel wherever needed over the textile surface so that, through pattern design, embroidery is the only textile technology in which threads can be trailed arranged in any direction. With the aid of embroidery, through fiber orientation, fiber-composite components can be created to withstand complex forces. When compared to standard textile technologies, is that reinforcement threads can be arranged direction, i.e. at any angle between 0° to 360°. Thus, embroidery allows an accumulation of reinforcement material by repeated embroidery across the same place. Through this repetition, even multilayer and 3D structure can be formed.
Although there is a hug advantage, the application of this technology into the fields of wearable textile, medical etc., has not been touched. This is particularly advantageous with relatively small motifs. As opposed to weaving, where threads are arranged at rigid angles, embroidery also enables rounded patterns. Additionally, made-up embroidery goods are dimensionally stable -unlike knitted fabrics. A further particularity of embroidery is that threads can be placed on top of one another, achieving threedimensional characteristics. Modern embroidery machines are equipped with color change devices, enabling switching from one material component to another during production.
Notably, many conductive yarns are too fragile to survive the many trips through the take-up mechanism of the needle thread of a sewing machine and must be used as bobbin threads. Some manufacturers report that conductive thread pass as much as 70 times through the needle before being embedded into the garment. Stitching a conductive pathway on the surface of a textile also requires that the pathway be electrically isolated in places where conductor cross each other and sometimes also be insulated from the outside so that the circuit is not affected by external moisture, perspiration and other factors, as mentioned in the various scenarios before and even the illustration listed in Figure 8.
It is also important that conductors not come into contact when the garment is folded, and so that the wearer is protected from any electrical shocks. For example, adjusting the tension on a lockstitch machine can allow the conductive yarn to float on one side of the fabric without passing through to the other side during each other without coming into contact by travelling on opposite side of the fabric. Stitched connective parts can also be insulated after sewing by laminating a protective fabric, film or coating over the stitching.
Conclusion
For more Lupine Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
For more fashion and textile research journal articles Please Click Here:
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers
Follow on Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/lupinepublishers
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.