Lupine Publishers | Journal of Clinical & Community Medicine
Abstract
Health is the level of functional and metabolic efficiency of a living being. in humans, it is the general condition of person in mind, body and spirit, usually meaning to being free illness, injury or pain. With the increase in urbanization, many cities around the world are experiencing a very rapid growth in the number of vehicles which lead to serious traffic congestion problems. This is the reasons to accept that occupational environment also plays a major role on the health of the exposed. The health hazard get more sever when the duration of exposure increases. This fact is more important in situations as the personnel engaged in traffic duty. The traffic is exposed to vehicular pollution in varied degrees. Among all of them traffic police are unduly and chronically expose to vehicular exhaust pollutants as they remain on duties for longer periods.
Traffic policemen had to undergo physical strain in on environmental polluted by fumes, exhausted of vehicles, use of blowing horns, blow of dust in the air by a speeding vehicle.
The present study shows that traffic policemen and office worker have not better nutritional status there are deficient nutrient intake and many health problems. The possible reasons are poor physical activity, work pressure, pollution, long hours in standing position and lack of knowledge OF nutrients. There are lack of deficiency in calcium, β-carotene, and protein. The fat intake was high.
Introduction
Health is the level of functional and metabolic efficiency of a living being. in humans, it is the general condition of person in mind, body and spirit, usually meaning to being free illness, injury or pain (as in “good health”). The world health organization defined health in its broader sense in 1946 as “a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”. The maintenance and promotion of health is achieved through different combination of physical, mental and social wellbeing, together sometimes referred to as the “health triangle”.
With the increase in urbanization, many cities around the world are experiencing a very rapid growth in the number of vehicles which lead to serious traffic congestion problems. To ensure a steady move on the traffic congestion, the traffic police have work in midst of hundreds of noisy and polluting vehicles throughout their working hours.
This is the reasons to accept that occupational environment also plays a major role on the health of the exposed. The health hazard get more sever when the duration of exposure increases. This fact is more important in situations as the personnel engaged in traffic duty.
The traffic is exposed to vehicular pollution in varied degrees. Among all of them traffic police are unduly and chronically expose to vehicular exhaust pollutants as they remain on duties for longer periods [1].
Nowadays, noise pollution is considered as one of the main problems of urban communities which has many hazardous effects on the urban environment and may results in a great deals of cost on the society [2] traffic can be considered as the main source of noise pollution in large cities. According to the researches, noise pollution caused by traffic is one of the major problems in the southern large cities of Sweden. In another research conducted in 2004 in the same country, in addition to the big cities of Sweden, the researchers have demonstrated that noise effects will limit the episodic memory [3] . The traffic policemen in metropolises are the most affected groups exposed to this dangerous factor during their working hours and in their leisure time. Ingle et al. [4] have been policemen measured the noise dose received by this group as 88 dB and, in some cases, it has been increased up to even 100 dB [4]. Statistic results published by organization for economic Co-operation and Development( OECD) in 1994 specified that more than 17 million people in France are exposed to sounds louder than 55Db during 8-20 hours of their lives, whereas the minimum standard noise for the problems of noise pollution in the environment is 55dB [5]. Canadian hearing society (CHS) researchers had considered urban environment as crowded, busy and noisy. Jack hammers pounding, sirens whining, alarms ringing, subway trains screeching, aircraft zooming overhead, car horns honking are a few of the annoying and potentially hazardous sounds face to dwellers. Moreover, it was concluded that the noise in some parts of these cities is so much that can lead to long- lasting and effects on the citizens and in places like masonry workshops and the shopping centres as 81 dB. Regarding to the sound standards 9 less than 55 dB) determined by world health organization (WHO), studying of the urban environmental noise become significant [5]. In a similar research conducted in Spain, it was demonstrated that the noise resulted from traffic can lead to physical and mental effects on the individuals stated that the speed of the vehicles, the traffic load, the number of trucks and the road surface were also the main factors of traffic noise in Beijing.
Materials and Methods
A. General information: information regarding general profile of respondent was collected by interviewing using standard questionnaire of information, age sex, occupation, type of work, hours of work per day, place and shift etc.
B. Study population: Traffic policemen working in Kanpur city.
C. Sample selection: sample was selected by purposive random sample techniques total 150 respondents was selected, 90 traffic policemen and 60 traffic policemen from office.
D. Nature of Job:
Traffic policemen- traffic policemen worked for 8 hours continuously working days 6 days (one week) for working this is nature of work continuously standing on land of city day come in to contact of outdoor exposed to vehicular exhaust pollution, and physical or chemical agent at their work place.
Office worker: office workers doing 8 hours a day for 6 days( one week) working in room or chamber so they do not exposed to vehicular exhaust pollution, noise pollution or any other physical, chemical agents at work place.
E. Clinical Examination
It is important practical method for assessing the nutritional status of community and the method is based on examination for changes believed to be related to inadequate nutrition. Clinical examination consists of physical examination. In order to find nutritional adequacy clinical examination was done. Hair was examined for lock of lustre, thinness, easy pluck ability etc. Face was examined for diffuse dispigmentation, dry face. Eyes were examined for conjuctival xerosis, bitot spot. Lips are examined for angular stometitis, glositis. Skin was examined for roughness, dryness, and dispigmentation. Tongue was examined for magenta tongue, pigmented and row tongue. Gums were examined for purplish swelling, bleeding gums. Nails were examined for shine less and normal.
F. Nutritional information: The present study nutritional information and diet survey was conducted by using repeated twenty four recall method and food frequency method.
G. Food frequency methods: the respondent was also asked frequency of intake of various food groups during interview of session. Frequency of consumption of non vegetarian food was also noted.
H. Statistical analysis: Data was analysed using
a. Percentage-
b. Chi-square test
c. Correlation coefficient
Deficient Percent = RDA-nutrient(average)/RDA ˟ 100
Result and Discussion
Clinical assessment
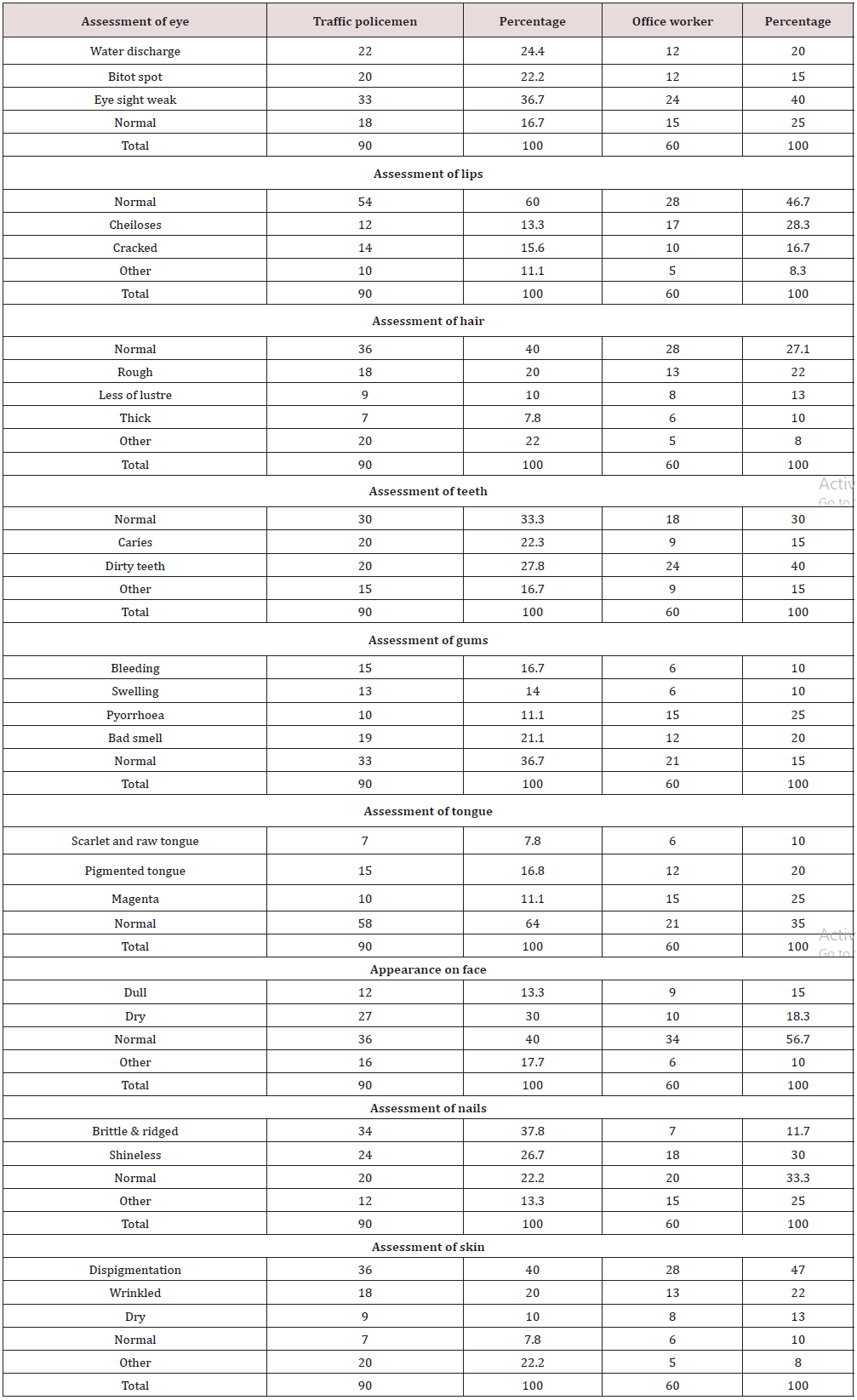
Distribution of respondent on the basis of symptoms
The table 1 reveals distribution of respondents on the basis of eye symptoms. In traffic policemen group 24.4 percent respondents were having water discharge, 22.2 percent respondents were having bitot spot, 26.7 percent respondents were having eye sight weak, 16.7 percent respondents were having normal eye. In office worker 20 percent respondents were having water discharge, 15 percent respondents were having bitot spot, 40 percent respondents were having eye sight weak and 25 percent respondents were having normal eyes [6, 7].
It found in the table distribution of respondents on the basis of assessment of lips. In traffic policemen group maximum 60 percent respondents were having normal lips, 13.3 percent respondents were having cheilosis and 15.6 percent respondents were having cracked 11.1percent respondent were having normal lips.
In office worker group maximum 46.7 percent respondents were having normal lips 28.3 percent respondents were having cheiloses lips 16.7 percent respondents were having cracked lips. 8.3 percent respondents were having normal lips.
The assessment of hair of the respondent table reveals that in traffic policemen group, maximum 40 percent respondent were having normal hair, 20 percent respondents were having rough hair,10 percent were having loss of lustre their 7.8 percent respondents were having thick hair 22.2 percent respondents were having other hair problem. Office worker group maximum 47 percent respondents were having normal hair, 22 percent respondents were having rough hair, 13 percent respondents were having loss of lustre hair 10 percent respondents were having thick hair, 8 percent respondent were having no other problems of hair.
Table 1 shown in traffic policemen group maximum 33.3 percent respondents were have normal teeth,22.2 percent were have carries in their teeth, 27.8 percent respondents were have dirty teeth, 16.7 percent respondents were have other related to teeth problem.
In office worker maximum 30 percent were having normal teeth, 15 percent respondents were have carries in hair teeth, 40 percent respondents were have dirty teeth, 15 percent respondents were have other problem related to teeth.
Table 1 shown in the distribution of respondents on the basis of gums. In traffic policemen group maximum 36.7 percent respondents were having normal gums, 16.7 percent respondents were having bleeding gums, 14.4 percent respondents were having swelling gums, and 11.1 percent respondents were having pyorrhoea problem in gums. 21.1 percent respondents were having bad smell problems in gums. In office worker group maximum 35 percent respondents were having normal gums, 10 percent respondents were having swelling in the gums, 20 percent respondents were having bad smell in gums.
Assessment of tongue of the respondent table reveals that in traffic policemen group, 7.8 percent respondents were having scarlet and raw tongue, 16.8 percent respondents were have pigmented tongue, 11.1 percent respondents were having magenta tongue, maximum 64.4 percent respondents were having normal.
Office worker group 10 percent respondents were having scarlet and raw tongue, 20 percent respondents were having pigmented tongue, 26 percent respondents having magenta tongue, maximum 35 percent respondents having normal tongue.
The table 1 reveals distribution of respondents on the basis of appearance of face, in traffic policemen group of maximum 40 percent respondents were having normal face, 13.3 percent respondents were having dull face, 30 percent respondents were having dry face, 17.7 percent respondents were indicated other symptoms of face.
In office worker group maximum 56.7 percent respondents were having normal face, 15 percent respondents were having dull face, 18.3 percent respondents were having dry face, 10 percent respondents were indicated other symptoms of face.
In the assessment of respondents on the basis of nails the table indicate in traffic policemen group 37.8 percent respondents were having brittle and ridged nail, 26.7 percent respondents were having having shineless nails, 22.2 percent respondents were having normal nails, 13.3 percent having other nails problem. In office worker group 11.7 percent respondents were having brittle and ridged and 30 percent respondents were having shineless nails, 33.3 percent respondents were having normal nails and 25 percent respondents having other nails problems.
In the assessment of respondents on the basis of skin the table indicate in traffic policemen group 36 percent respondents were having dispigmented skin, 18 percent respondents were having wrinkled skin, 10 percent respondents having dry skin, 7.8 percent respondents having normal skin and 22.2 percent were having other skin problem. Office worker group 47 percent respondents were having dispigmented skin, 22 percent respondents having dry skin, 10 percent respondents having normal skin and 8 percent having other skin problem.
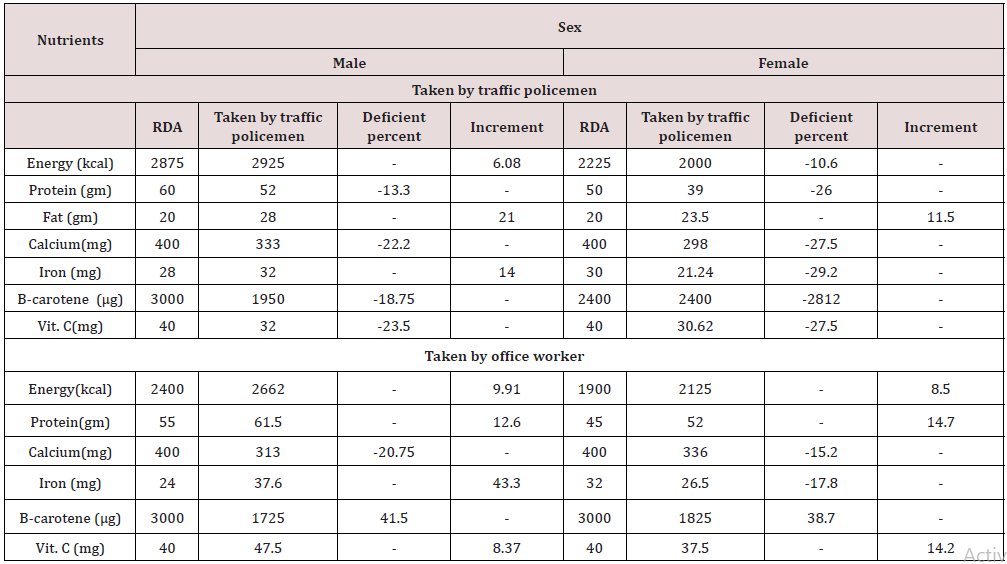
Intake of Nutrient Compared with Recommended Dietary Allowance
(Table 2)
The information collected by survey which represented the difference of intake of nutrients in traffic police male and female .the survey value compared with RDA value and found deficient percent and non- deficient percent
Energy value compared to RDA value found that 6.08 percent increment in traffic police male and 10.6 percent deficient in traffic police female. Whereas, the protein intake value compared with RDA value found deficient 13.3 percent in traffic police female. After the value fat intake compared with RDA and found 21 percent in traffic police male and 11.15 percent increment in traffic police female. In calcium comparison found 22.2 percent deficient in traffic police male and 27.5 percent deficient in traffic police female. The iron value comparison with RDA value found 14 percent increment in traffic police male and 29.2 percent deficient police female. Β-carotene value compared with RDA value 18.75 percent deficient in traffic police male and 28.12 percent deficient in traffic police female. Vitamin-C value compared with RDA value 23.5 percent deficient in traffic police male and 27.5 percent deficient in traffic police female.
In the difference of nutrient intake in office worker, male and female. The survey value compared with RDA value and found deficient percent and increment energy value to RDA value found that 9.91 percent increment in office worker male and 8.5 percent increment in office worker female whereas, the protein intake value compared with RDA 12.6 increment found in office worker male and 14.7 increments found in office worker female.
In calcium comparison found 20.75 percent deficient in office worker male and 15.2 percent deficient in office worker female. The iron value comparison with RDA found 43.3 percent office worker female beta- carotene compared with RDA value 41.5 percent deficient in office worker male and 38.7 percent deficient in B- carotene. Vitamin-c value compared with RDA value 8.37 percent increment in office worker male and 74.5 percent increment in office worker female.
Conclusions
Health is very important for everybody. The work environment consistories on important part of mans total environment, this fact is more important in situation as the personal engaged in traffic duty.
Traffic policemen had to undergo physical strain in on environmental polluted by fumes, exhausted of vehicles, use of blowing horns, blow of dust in the air by a speeding vehicle.
The present study shows that traffic policemen and office worker have not better nutritional status there are deficient nutrient intake and many health problems. The possible reasons are poor physical activity, work pressure, pollution, long hours in standing position and lack of knowledge OF nutrients. There are lack of deficiency in calcium, β-carotene, and pro tein. The fat intake was high.
Read More about Lupine Publishers Journal of Clinical & Community Medicine Please Click on Below Link:
https://journalofclinicalcommunitymedicine.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.