Lupine Publishers| Journal of Orthopedics and Sports Medicine
Abstract
Background: The Latarjet procedure may be amenable to outpatient elective surgery as it is often performed on young and healthy patients. Thus, ambulatory surgery for Latarjet procedure is recently rapidly increasing in France with very few validation studies. This feasibility study presents early adverse events following outpatient Latarjet surgery compared to Latarjet surgery performed as an inpatient procedure.
Hypothesis: There is no difference between outpatient or inpatient Latarjet procedure.
Patients and Methods: Thirty patients operated on an outpatient basis and prospectively followed were compared to 30 patients operated on an inpatient basis. All procedures were performed by the same surgeon. Complication rates as well as clinical outcomes at one year were compared between groups.
Results: Post-operative hematomas which did not require surgery occurred more frequently in outpatient group in which no drain was used. No other differences occurred between groups. All outpatients but one was satisfied with the procedure.
Discusion: The latarjet procedure was found to be safe when performed on an outpatient basis. The addition of wax to the base of the coracoid seemed to diminish hematoma formation.
Level of Evidence: level III
Keywords: Shoulder; Latarjet; Instability; Complications; Ambulatory surgery
Introduction
Outpatient surgery provides benefits to patients including a decreased exposure to nosocomial infections, a higher rate of satisfaction [1], and a up to a 68% decrease in direct costs [2]. The Latarjet procedure is now frequently performed on an outpatient basis in up to one third of cases in France in 2017 (Figure 1).
However, the literature regarding the feasibility of outpatient Latarjet surgery is very poor and there is still a need of validation studies [3]. Our aim was to confirm the feasibility of the outpatient Latarjet procedure by comparing the incidence of adverse events and clinical outcomes between patients who underwent inpatient or outpatient Latarjet surgery. Our hypothesis was that the outpatient procedure is both feasible and safe.
Patients and methods
Patients
Study inclusion criteria were as follows: patients were considered if they had a diagnosis of recurrent anterior shoulder instability; were deemed candidates for surgical stabilization; had not undergone prior shoulder surgery, and did not have any significant shoulder co-morbidities. All patients underwent primary surgery for anterior shoulder instability using transfer of the coracoid process (Latarjet procedure). All procedures were performed by a Single Surgeon (SZ). Thirty consecutive patients underwent surgery on an outpatient basis between 2013 and 2017 and were prospectively followed. This group was compared to 30 patients who underwent the Latarjet procedure on an inpatient basis between 2007 and 2012 by the same surgeon.
Surgical protocolA standardized general anaesthesia protocol was followed. An additional interscalene block was administered under ultrasound guidance (single bolus of 20ml of 0.375% ropivacaine) associated with 8mg of a dexamethasone intravenous injection. An open minimally invasive technique was used. The osteotomy of the coracoid process was performed through a deltopectoral approach after the coraco-acromial ligament and pectoralis minor tendon were released and following conjoint tendon exposure and dissection. All harvested coracoid grafts were a minimum of 20mm in length. The subscapularis tendon and muscle was split horizontally. Following glenohumeral capsulotomy, bone on the ventral aspect of the coracoid process and on the anteroinferior aspect of the glenoid rim was decorticated. Any remaining anteroinferior bone bankart fragments were resected. The ventral aspect of the coracoid graft was fixed to the inferior portion of the anterior scapular neck such that the transplant was level with the anterior glenoid rim. The coracoid process was drilled with two 3.5mm holes and fixed with two 3.5 diameter cortical screws; whilst the glenoid neck was drilled with 2.5mm holes to enable compression.
Care was taken to avoid lateral overhang of the graft across the joint line as described by Alain et al. [4]. No additional capsular suture was used. The subscapularis tendon was closed lateral to the graft. Traction on the coracoid graft was avoided all along the procedure to decrease the risk of musculocutaneous nerve injury. The wound was closed in layers with continuous absorbable skin suture. All inpatients had a suction drain inserted. No drain was used in the outpatient group. Sling immobilization was used for one week following surgery. Simple activites of daily living (shower, eating, writing) were immediately permitted. Following one week, self-assisted stretching in all planes was permitted. Running and swimming were allowed after two months, and high-risk sports (rugby, judo…) were allowed after 4 months. All patients were assessed on post-operative day one (by telephone for outpatients); further assessments took place at 1 week, 1 month, 4 months and 12 months post-operative.
Evaluation criteria and statistical analyses
Readmission rates and early complications were recorded. Shoulder range of motion, recurrent instability, persistent subjective apprehension and shoulder pain were compared between groups at one year. Satisfaction rate with the outpatient protocol was assessed. Continuous variables were compared with the independent t-test and categorical variables with the Fisher exact test; statistical significance was set at 0.05.
Results
The 2 groups were comparable at baseline (Table 1). Mean hospital stay in the inpatient group was 2.2±0.4 days. One admission for one night occurred in the outpatient group due to dizziness which resolved without further treatment. No complications occurred related to the interscalene block. There were no reoperations, no nerve injuries and no infections in the series.
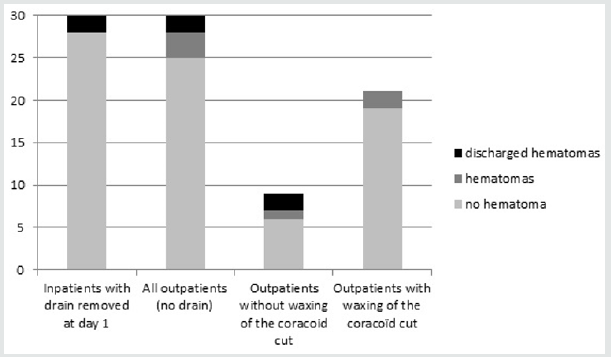
In the inpatient group, drained blood volume prior to drain removal was negligible in 18 patients, less than 100cc in 11 patients and > 100 cc in one patient. All drains were removed on post-operative day one. Seven hematomas occurred within the first 3 weeks following surgery: two in the inpatient group and five in the outpatient group (Figure 2). Four of these hematomas, two in each group, discharged and healed spontaneously. All others healed spontaneously without fistulization. One of these hematomas occurred in a patient with the Factor V Leiden defect (outpatient group). Three of these hematomas, with fistulization twice, occurred in the first 9 patients in the outpatient group and induced a change in the surgical technique. In the following 21 patients, prior to closure, the osteotomy of the coracoid feet was explored, washed and waxed prior to closure during which time a blood clot was typically found. Wax was never used for patients in the inpatient group.
Figure 1: Latarjet procedures statistics in France between 2013 and 2017 (ATIH, technical agency of information on hospitalization, www.atih.sante.fr).
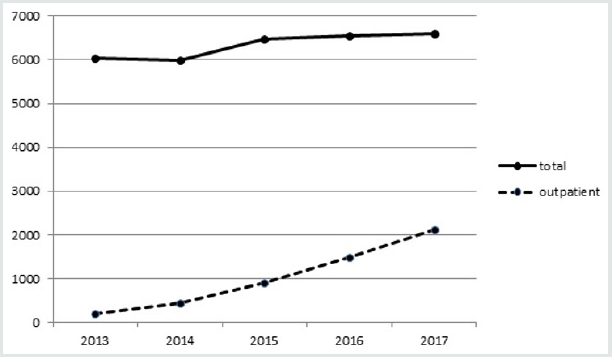
Figure 2: Hematomas formation by group. There was more hematomas in the outpatient group (p<0.01), all hematomas healed spontaneously.
All outpatients but one were satisfied with the procedure. One patient indicated that he would have preferred a one night hospital stay due to postoperative discomfort. At final 12 month followup, no patient had experienced further instability. Six patients answered positively for subjective persistent apprehension in both group (20%). One third of patients of each group have reported occasional shoulder pain. Loss of external rotation was found in half of patients of each group (Table 1).

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.