Lupine Publishers | Journal of Surgery & Case Studies
Abstract
Introduction: A series of 78 laparoscopic hernioplasties performed in the General Teaching Hospital “Enrique Cabrera”. Objective: To determine perioperative events, surgical complications and the evaluation of the pain referred by the operated patients.
Methods: Between January 2012 and December 2018, 78 hernioplasties were performed laparoscopic in 60 patients; 18 had bilateral inguinales hernias. He collected the variables: age, sex, type of hernia, perioperative events and complications, and a pain scale was applied. A database was filled and processed statistically.
Results: The male sex predominated in a 5:1 ratio, the surgical time average was 53.5 minutes for unilateral hernias and 71.3 minutes for the bilateral ones. The most frequent complication in the transoperative period was bleeding lower in 27.0%, and in the postoperative period the hematoma was in 15.3%, it recurred two hernias (2.5%). At 15 days after surgery, 93.3% of theoperated did not complain of pain, but the social and labor reintegration was of only 34% of patients.
Conclusion: laparoscopic inguinal hernioplasty is a therapeutic option more, mainly in patients with bilateral and reproduced hernias.
Keywords:Laparoscopic Hernioplasty; Inguinal Hernia; Hernia Recurrence
Introduction
Since the concept of endoscopic inguinal hernia repair was first described by Ger R [1] in 1982, the endoscopic techniques are gone modifying, going through a time when failures and complications -united to high cost-exceeded initial enthusiasm [2]. Laparoscopic hernioplasty (HL) has been gaining popularity in the last decade, and numerous controlled studies appear in the literature comparing the laparoscopic techniques with conventional techniques [3-7]. In recent years, HL, despite consolidated as a therapeutic option to consider. The advantages of this have been demonstrated method in bilateral hernias, relapsed and in the active labor subject, that requires a precocious labor reintegration [5-7].
Methods
Between June 2012 and June 2018, a prospective descriptive study of Longitudinal section of 60 patients operated by hernia endoscopy of the region inguinal, in the Department of Surgery of the General Teaching Hospital “Enrique Cabrera”. The inclusion criteria were: - Patients who agreed with the type of surgical intervention and the study, and They gave their informed consent. Patients older than 30 years classified ASA I-III, without contraindications anesthetics for laparoscopic interventions.
a) Patients classified as Nyhus III and IV. Exclusion criteria.
b) Patients with previous surgical wounds in the inguinal region to operate, not dependent on inguinal hernias reproduced.
c) Inguinal hernias complicated, irreducible or slipped.
The surgical techniques were: laparoscopic inguinal hernioplasty completely extraperitoneal (TEP) of total extraperitoneal English and inguinal hernioplasty laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneum (TAPP) preperitoneal), and one or the other was performed, at the discretion of the main surgeon. The TEP technique was executed with some variants such as: not using the trocar balloon, the preperitoneal space was decoloured by means of the 0º laparoscope, and the insufflation of CO2 at 13 mmHg. In patients with large herniated rings, placed a polypropylene cone in the hernia defect and then a 15 x 12 cm polypropylene prosthesis. There was no need to fix with clips the tights. The TAPP technique was performed on a regular basis [8]. In the immediate postoperative period, the scale of visual pain analog scale was applied (VAS), [9] and a value was assigned to pain through “caritas”, which starts very cheerful (value I) until very sad (value X). The quantification of pain was repeated in consultation at 7, 15 days and one month after surgery.
Results
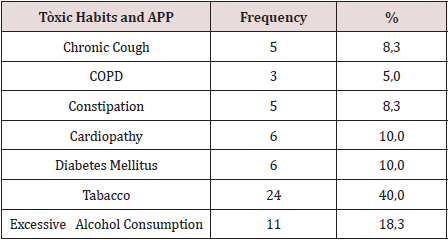
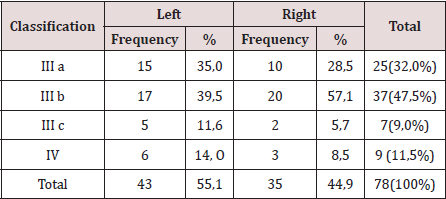
There were operated 78 hernias in 60 patients (18 patients [30.0%] suffered from bilateral hernias, 69 primary hernias and 9 reproduced hernias). The average of age was 55.6 years, the youngest patient was 30 years and the oldest was 77 years, but the majority (12 patients) were in the fifth decade of life. The male sex predominated in 82.9%, which represented a relationship man / woman of 5: 1. 42.9% of patients performed large efforts habitual physicists. The pathological history of the patients (Table 1). It is observed that 24 patients (40.0%) consumed tobacco, and in 11 an excessive consumption of alcohol was collected 18.3%. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Table 2). The distribution of the series according to the Nyhus classification. Right hernias predominated (55.1%), the indirect variety with large dilation of the ring and destruction of the posterior wall (IIIb) was the most frequent (37 hernias), and 7 femorales hernias and 9 recurrent hernias were operated 73 PET (93.6%) and 5 TAPP (6.4%) were performed. Two of the patients in whom a TEP technique was started were converted to a conventional prosthetic technique by accidental perforation of the peritoneum, passing the CO2 into the peritoneal cavity, and consequently, the loss of the preperitoneal surgical space. Of the 5 TAPP repairs, 3 of them were in the course of a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and another was the conversion of a failed PET technique. The average surgical time of unilateral hernias was 53.5 min, with a minimum of 25 min and a maximum of 120 min. In bilateral repairs, the average surgical time was 71.3 min, and a minimum of 40 and a maximum was observed. of 110 minutes.
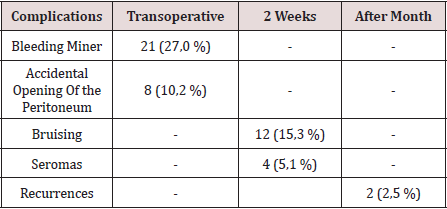
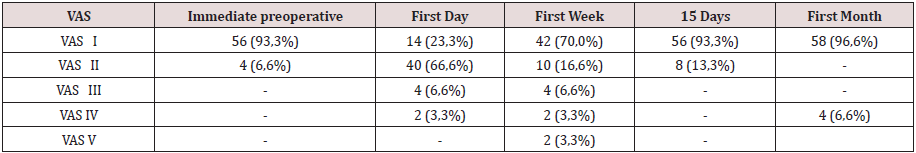
The hospital stay was less than 24 h in 50 patients (71.4%), in 5 it extended from 24 to 48 h, and in 5 to more than 48 hours. The most frequent complication in the transoperative period (Table 3) was minor bleeding in 21 repairs (27.0%) that gave rise to 12 hematomas (15.3%). No complications were observed after the second week, but two patients suffered recurrences (2.5%), more than two months after surgery. The application and evaluation of the VAS scale (Table 4). In the immediate postoperative period, after the patient recovered from anesthesia, 56 individuals (93.3%) were classified as VAS I, and 4 as VAS II. Twenty-four hours after surgery, 14 patients (23.3%) were classified as VAS I, 40 (66.6%) as VASII, 4 patients as VAS III and 2 VAS IV. In the consultation of the first week of postoperatively, 42 patients (70.0%) were classified as VAS I and [10] as VAS II, and two patients with moderate pain (VAS V) appeared in this period. Fifteen days after surgery, 56 individuals (93.3%) were VAS I and a month were 58 (96.6%). The incorporation to the usual activities, including work, was 3 patients a week after surgery, at 15 days they were 19 patients (31.6%) and 54 patients a month (90.0%).
Discussion
Currently, with the improvement of laparoscopic techniques, these are outlined as safe, reproducible and as a therapeutic option regardless of the age of the patient; nevertheless, the evaluation of the individual must be correct and meticulous in the preoperative period, specifically cardiorespiratory function, since with the TEP method a working space is created between the sheets of the crosssection sheet, richly vascularized, so that absorption and elimination of CO2 is greater than that produced in the peritoneal cavity during the performance of the pneumoperitoneum [10]. Although men predominated, there was a slight increase in women in the series with respect to other authors, [3-5] which could have been due to the inclusion in the study of 3 women who underwent the diagnosis of inguinal hernia, in the course of a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In laparoscopic practice, it is not uncommon finding of hernia defects diagnosed in the transoperative, in men and women, the latter basically with a history of gynecological disorders. Although the usefulness of hernia repairs in asymptomatic patients is questioned in some articles, [11,12] the authors consider that it would be beneficial for the patient, if conditions permit, the repair of the hernia defect by the TAPP method. The relationship between the hernia disease and the physical efforts, is classic from the Cooper era [1]. In the series, 68% of the patients performed physical activities involving large and medium efforts, and also analyzing the multifactorial character in the pathogenesis of hernia disease, was striking, that approximately half of the patients operated on were smokers, a factor that influences the metabolism of collagen, significantly linked to hernia recurrences [13]. The majority of the repairs were by means of the PET technique, and we consider, as other authors [10,14 -19], that although the TAPP technique brings us closer to the area from a family perspective to the surgeon (peritoneal cavity) and facilitates the so-called “learning curve”, the hernial disease - considering it a parietal defect- should be given solution from this same plane to avoid the likelihood of serious complications of intrabdominal , and to leave the transperitoneal method as a tactical resource when the totally extraperitoneal method is unsuccessful.
The average surgical time was similar to other series [3-6]. It is known that this tends to decrease when the surgical team gains experience [16]. The largest surgical time recorded was in a patient, who was started with a PET technique, but Due to technical difficulties, it was converted to a conventional posterior repair. The fundamental complications were in relation to minor bleeding in the transoperative period and postoperative hematomas. In 3 patients it was necessary to drain the hematoma due to the discomfort caused, however, in the rest of the patients with hematomas and seromas they were treated with conservative measures. In two patients, the recurrence occurred 2 months after surgery, which was interpreted as a technical error. Our results coincide with numerous studies [3-7], that indicate the least postoperative pain of the minimum access techniques, as well as a prompt social and labor reincorporation of the patients. Despite the fact that 70% and 93.3% a week and 15 days postoperatively, respectively, had no pain or discomfort were minimal, only [18] individuals (30%) were incorporated into their usual activities before 15 days. These results contrast with other studies that report a return to work and social activities between 10-15 postoperative days, 4-17- although it is likely that some sociocultural factors are influencing these results. It can be concluded by noting that laparoscopic inguinal hernioplasty is another therapeutic option, mainly in patients with bilateral and reproduced hernias. In the series there were no major transoperative or postoperative complications, only minor bleeding and bruising were present. Most patients were not afflicted by pain 2 weeks postoperatively, however, return to social and labor activities after 15 days was low [18-20].
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Surgery & Case Studies Please Click on Below Link:
https://surgery-casestudies-lupine-publishers.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.