Lupine
Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Journal
Spatial analysis in GIS Wednesday is based on complex
techniques, the results of which depend on the raw data. One of
the fundamentals of spatial analysis techniques based on digital
hypsometric model is the development of maps of the angles.
She gained widespread use, from morphogenetic and geologicalengineering
perspective to the agrarian and territorial planning.
Progress of Research and Discussion of Materials
Program Arc Map provides the ability to quickly prepare this
type of cards based on raster model hypsometric territory. To
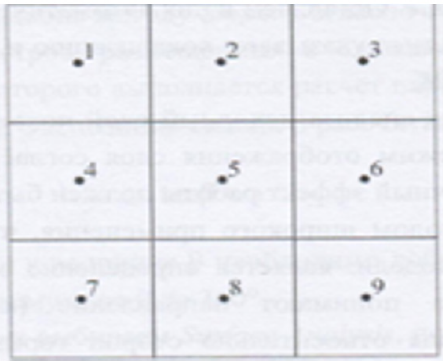
calculate the slope of a surface that is specific to a particular screen,
used values of absolute height, raised eight surrounding screens
(Figure 1). The calculated values of the two parameters (ɑ and (b)),
proportional average slant of slope (respectively on the x and y
axis) according to the following formulae:
Where is:
(h)1 = the absolute height of the surface of the territory in (i)
-OM image according to (Figure 1).
L = raster measurement.
The angle of the slope, plant in the central point is cal
tan ɑ= √a2 + b2 (2).
a) In the menu Spatial Analyst pick Surfase Analysis, then
Slopethat will lead to opening the window method.
b) With list boxes Input surface Choose created a digital
model of the hypsometric of Azerbaijan.
c) The main unit can be marked graphs slope measurement
slope on the resultant map-in variant degrees ( Degree) or as a
percentage (option) Percent
d) Graphs Z Factor and Output cell size perform the same
role as in the Hillshade. Leave them automatic size.
e) In the graph Output raster point localization and name of
the source file, then- OK.
f) After completion of the analysis of the source layer
appears in the map image.
g) Change the layer display mode according to the technique
described previously.
h) The final effect should be similar to (Figure 2).
i) The following method of broad application that is based
on digital hypsometric model is the definition of exposure [1].
Under slope Exposition, understand the direction (azimuth)
slope steepness of most to the sides of the horizon.
This option is very important for those kinds of analysis that
takes into account the difference of thermal balance of the northern
and southern slopes.
This is the initial value for aspects such as the time of
occurrence of snow cover duration of vegetation period etc. The
method of calculation is similar to the method Slope . It also used
high-altitude data from screens placed in the immediate vicinity of
the Central screen, for which the calculation of parameters (a) and
(b) (in accordance with identical formulas) [2].
Exposition of slopeis calculated as:
tan ß=a/b (3)
If (b) positively, the largest Add 180°, that allows to take into
account the magnitude of the azimuth from 0 to 360°.
a) In menu Spatial Analyst choose a Surface Analysis, then
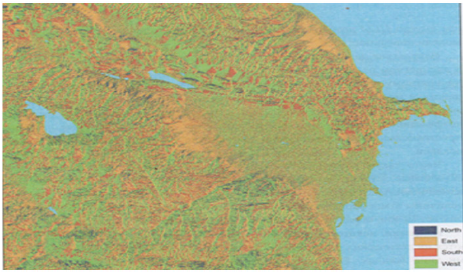
Aspect-method dialog box appears (Figure 3)
Figure 3: Angular slopes map developed in accordance
with method S lope based on a digital model of Azerbaijan
hypsometric.

b) In box Input surface traditionally make the filename
digitally hypsometric model.
c) In box Output cell size leave unattended.
In box Output raster denote localization and name of the source
file, click OK to start following their completion, payments to the
image will be added effective map. After you change the display card
is similar to (Figure 3). Next, consider the way to an integrated spatial
analysis based on raster maps. For example, suppose you want to
select a specific localization hypothetical potential investments on
the territory of Azerbaijan. Investor demands that the investing
territory meets certain conditions. First, the angle of the slopes
in the territory’s investment should not exceed 10°. Secondly, the
investment should be within the absolute height of surface from
100 to 500 mnm. Using GIS and digital hypsometric model of
Azerbaijan (with derived layers), the definition of localizations of
this investment takes a few minutes. In menu Spatial Analyst toolbar
Select position Raster Calculator. A dialog box appears, represented
in the left part of the window, in the Layers highlighted all raster
layers project. With right sides are mathematical logical operators
that can be used for entering formulas. The formulas are based on
arithmetic operators, and the results have a numeric expression.
For example, if you want to double increase digital hypsometric
model, it is possible to formulate a simple expression: [CGM]. where
instead of CGM, you must enter the name of the selected raster layer
surface model. As a result of this operation received a raster map,
where each point in discrete space is assigned a numerical value,
which corresponds to doubling the height of the territory. Such
arithmetic operations can be applied to other sectors. For example,
having a layer of embossed field precipitation, as well as layer with
spatial distribution of filtration coefficient, obtained by multiplying
the two layers you can obtain the spatial distribution of effective
infiltration of precipitation. Often also used the differencing
method. In this way, create a differential maps that document the
temporarily-spatial variability of the investigated phenomenon. For
example, as a result of the seizure of average precipitation from the
actual over the past two years, it is possible to define the territory
increases and regression of this phenomenon [4-6].
Use this type of expression to identify the territory within
Azerbaijan, which satisfies the conditions of investra. First define
the territory where the inclination does not exceed slopes 100.
This requires the formulation of the next task
[Slope] < = 10. (4)
Where on the graph Slope you must submit the name of a
bitmap layer with angles of inclination of slopes.
Formulation of issues using Windows Raster Calculator is
simple enough:
i. In the graph Layers Select the name of the layer with
the angles of inclination of slopes. Note that added layer
automatically enclosed in quotation marks.
ii. Of the symbols of the operators choose < =. This results in
adding this element to the expression.
Citation: RAE Aliyev ZH. Selected Methods of Spatial Analysis of
Soils of Azerbaijan. Open Acc J Envi Soi Sci 1(1)- 2018.
OAJESS.MS.ID.000103.
18
iii. Using digital signs in a window or on the keyboard, type
10 in the end of the expression.
iv. The formula is ready, you can go to to do so. Evaluate.
Upon completion of the calculations in the working area of the
project will add a new layer using the program Calculation . Layer is
only with greatness and 0 1.
Screens marked digital 1, satisfy the conditions of maximum
slope slopes up to 10 largest° . Now you must select the area that
meets the requirements of investra for its absolute height. To do
this, construct the following expression (5) [7-10]:
[CGM] > = 100 and [CGM] < = 500 (5)
On site CGM enter the name of a raster layer with digital
hypsometric model territory. For formulating expressions use
window Raster Calculator .
a) In Windows Raster Calculator Select layer with digital
hypsometric model of Azerbaijani territory in the graph Layers.
b) press the key with the operator > =
c) Enter the value 100
d) Push And
e) Again click on the layer name in the CGM graph Layers.
f) Push the button with the < = operator
g) Enter the value 500
h) Check the correctness of the formula and select Evaluate.
The result of the calculations is a raster layer named program
Calculation . 2. similar to the previous layer here showing screens
marked cifroj1 that identify the territory, where high-rise relevant
criteria. now you must connect both layers to define the territory
corresponding to two requirements-surface height and tilt. Use the
method the Raster Calculator [11-12].
a) press twice on the layer Calculation in the graph Layers.
b) Select the = operator
c) Enter the value 1.
d) Choose the logical operator And
e) twice click on layer Calculation2.
f) Select the = operator
g) Enter the value 1.
h) The final expression must be of the form:
[Calculation] = 1 & [Calculation2] = 1
i) Click on Evaluate. In the working area will be added a new layer with the designated (red) territory, which satisfies the
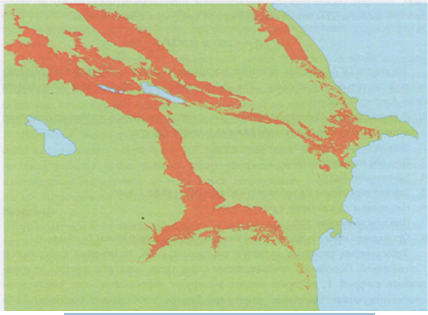
requirements of the investor (Figure 4) [13-15].
The resulting image points to a very extensive array, located in
the foothill zone of Azerbaijan. It is clear that in such a large territory
does not satisfy any investor to potential localization object. In this
regard, you can narrow the boundary parameters of each criterion.
For example, the choice of the territory where the inclination does
not exceed 1 degree. In the analysis process can also take into
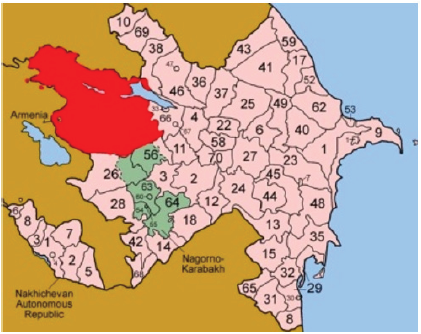
account additional criteria, such as location, investment plot at a
distance of not less than 500 m from the nearest coastline and 1000
m from the urban areas (Figure 5). The possibilities are endless
and depend solely on the needs of the user of GIS and spatial
information availability [15-18].
Figure 5: Result of the spatial analysis to define the
territory of Azerbaijan, the relevant requirements of the
investor.
Follow on Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/lupinepublishers
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.