Rheumatism is a systemic inflammatory disease of connective tissue
and joints with a predominantly affected heart. Children and young
people are ill mostly: women are 3 times more likely than men.
Therefore, the problem of rheumatism in pregnant women is quite common.
Keywords: Rheumatism; Pregnancy; Orthopedist
Etiology & Pathogenesis
The main etiological factor in acute forms of the disease is betahemolytic
streptococcus of group A [1]. In patients with prolonged
and continuously recurrent forms of rheumatic heart disease,
the association of the disease with streptococcus often fails to be
established. In such cases, the defeat of the heart, which fully meets
all the main criteria for rheumatism, apparently has a different
nature - allergic (not related to streptococcus or, in general,
infectious antigens), infectious-toxic, viral. Speaking of rheumatism,
it is implied that the process involves the musculoskeletal system
and the cardiovascular system [2]. Given this fact, it becomes
extremely clear that pregnancy with such extra genital pathology
should proceed under the compulsory supervision of not only the
obstetrician-gynecologist, but also the rheumatologist. According
to statistical data, pregnancy itself rarely leads to the development
of an unpleasant phenomenon of the future mother, such as
rheumatism.
Usually, women already suffer from this ailment, only during
pregnancy the disease worsens in 20% of women and causes many
pregnant women to seek medical help [3]. The development of
rheumatism is observed in the first months of pregnancy, when
there is a weakening of immunity and the body as a whole. This
indicates that the body is not able to withstand various diseases,
which are mostly infectious. Births also play a significant role in the
development of extra genital pathology. After all, it is well known
that after giving birth, the body is significantly weakened and
loses ability to fight against many diseases, including rheumatism.
It takes sufficient time for the body to recover and the woman to
return to her former strength. The most unpleasant thing is that if
rheumatism worsens at the initial stage of pregnancy, it can lead
to an interruption of the process, because any acute inflammation
occurring in the body requires mandatory medical intervention and the
admission of certain groups of drugs [4]. How rheumatism is
manifested and how can it happen in pregnant women? Most often
it is caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A.
The development of the rheumatic pathological process
consists of several stages:
a) a disease with sore throat, pharyngitis, scarlet fever, or
other ENT infection of streptococcal nature;
b) In response to the penetration of β-hemolytic
streptococcus, the immune system produces specific antibodies
- the so-called “antibodies”. C-reactive proteins;
c) In the presence of a genetic predisposition to rheumatism,
C-reactive proteins begin to attack their connective tissue
cells (similar antigens exist on their surface, as in hemolytic
streptococcus);
d) An autoimmune inflammatory process develops in
the affected area - most often in the joints, myocardium,
endocardium, vessels, etc. [5,6].
The provoking factors of exacerbation of rheumatism
during pregnancy are [7]:
a) Hypothermia;
b) Physiological Reduction of Immunity in early Pregnancy;
c) Bacterial and Viral Infections;
d) Stress;
e) Malnutrition;
f) Exacerbation of Existing Chronic Diseases;
g) Excessive Exposure to the sun.
Speaking about the symptoms of the disease, it should be
borne in mind that they are in some ways similar to those with
streptococcal angina and are characterized by [8,9]:
a) general weakness;
b) the appearance of pain in the heart;
c) often minor physical exertion can provoke shortness of
breath, rapid heart rate;
d) loss of appetite;
e) Joint pain, especially on days when the weather is
changing noticeably; increase in temperature.
Due to the fact that during pregnancy many corticosteroid
hormones are produced that have anti-inflammatory effect,
the signs of exacerbation of rheumatism are blurred and not
pronounced. With a heart form of rheumatism, pain in the heart
is more pronounced. As a rule, the joint form is combined with the
heart. It all starts with pain in the large joints. In this case, the pain
passes from one group of joints to another. The cutaneous form is
manifested in the appearance of characteristic pink rings on the
skin, which eventually pass Rheumatism of pregnant women can
lead to a condition like late toxicosis. With the exacerbation of
rheumatism, there is often an acute shortage of oxygen, which can
lead to placental vasculitis, changes in the placenta, intrauterine
hypoxia and hypotrophy. Given the possible complications, those
pregnant women who are at risk are kept under close supervision
throughout the process, right up to the birth itself. If a woman has
suffered several exacerbations of rheumatism, she should definitely
mention this at the first visit to the doctor of a woman’s consultation.
As a preventive measure, you must take care of acute infectious
diseases, and if they arise, immediately go to a doctor who will
prescribe an effective treatment. In addition, antirheumatic therapy
is performed in pregnant women who have undergone angina or
catarrh of the upper respiratory tract.
Diagnosis of rheumatism in pregnancy
Recognize and determine rheumatism in a pregnant woman
can only a doctor after the examination and analysis. Diagnosing
rheumatism is important in the first trimester. Because of the
dangers that rheumatism causes (especially if there is heart failure
and heart defects), it may be asked about the need for abortion. The
diagnosis of rheumatic carditis is based on ECG (electrocardiogram),
ultrasound of the heart [10]. It is necessary to consider those
cases when a number of pregnant women do not suspect about
the presence of rheumatism. To identify extra genital pathology,
laboratory (diagnostic) studies are mandatory. Speaking about the
complex of diagnostic examination, we mean the delivery of a blood
test, as well as ultrasound, an echocardiogram of the heart. These
indicators can give accurate information about whether a pregnant
woman suffers from rheumatism or not.
Particular attention is paid to increasing the heart rate. In
pregnant women suffering from a disease such as rheumatism, the
heart rate has a more pronounced picture than the usual (healthy).
Nevertheless, it should not be forgotten that in most cases this picture
may indicate more about the development of insufficiency
in pregnant blood circulation, rather than the development of
rheumatism. Therefore, several methods are used to obtain more
accurate and reliable information about the work of the heart.
In this case, an important role in the diagnosis is played by ECG
(electrocardiogram) indicators, such as: increase / flattening
/ broadening of the P-Q interval; serration of the tooth P; QRS
complex changes; slight or, conversely, a significant decrease in
the ST segment and T wave. In addition to the results of ECG and
ultrasound of the heart, blood tests are used to diagnose rheumatism.
Practice shows that rheumatism, especially if there is a tendency
to exacerbate it, leads to an increase in ESR (sedimentation rate
erythrocytes) to 35-50 mm / h. When conducting a biochemical
blood test in pregnancy, the main indicators are [11]:
a) C-reactive protein;
b) Hexose;
c) Ceruloplasmin;
d) Seromucoid;
e) Hydroxyproline;
f) A2-globulin.
As for the indicator, such as fibrinogen, which is determined
by the blood test, it is not given special attention, since it is always
elevated in pregnant women and does not indicate an increase in
rheumatism. Another issue is the identification of those pregnancy
periods in which one can expect activation of the rheumatic process.
Almost all authors agree that the most frequent exacerbation of
rheumatism occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy. The second
vulnerable period is postpartum; sometimes an exacerbation
occurs at a gestational age of 28-32 weeks, so it is reasonable to
conduct an anti-relapse treatment in these periods and especially
in the first 3 months of pregnancy and immediately after delivery.
It should be noted that the risk of exacerbation is not limited only
to the postpartum period. These people may come several months
after the birth, demanding special monitoring of this contingent of
women for a longer time (at least, up to 6-12 months).
Many pregnant women are wondering: why should the survey
be conducted at an early stage, that is, in the first months and
even weeks of pregnancy? The fact is that pregnant women with
rheumatism require serious treatment, especially if it is a question
of exacerbating it. If the treatment is serious enough, that is, the
expectant mother should take strong drugs, then the process should
be suspended. That is, in this case, it will be about the termination
of pregnancy. There is nothing comforting in this, of course, not, as
most of the pregnant women fall into depression and understand
that they do not promise birth in the near future. However, such
an approach to solving the problem is most appropriate, since
rheumatism has the ability to negatively affect the development and
formation of the baby’s future. To avoid any consequences, doctors
are advised to terminate the pregnancy, undergo a full course of
treatment and only then think about re-conception of the child.
Exacerbation of the rheumatic process during pregnancy, and even more so if a woman becomes pregnant with an active rheumatic
process, is fraught with the possibility of a number of complications
of pregnancy. Thus, according to the materials of the authors [12],
with an active rheumatic process, deviations from the normal
course of pregnancy are observed one and a half times more often
than with the inactive and pathological births - more than twofold.
Our observations confirm these data: premature termination
of pregnancy, late toxicosis, threatening fetal asphyxia, premature
discharge of amniotic fluid was more frequent. Of particular note
is the late toxicosis, which in patients with rheumatism often
occurs atypically, at a “normal” level of arterial pressure against the
background of impaired blood circulation, caused by activation of
the rheumatic process. If you recognize the allergic nature of late
toxicosis, you can understand why it often occurs with rheumatism.
In the case if rheumatism in pregnant women is mild, that is, there
is no exacerbation, and the issue of termination of pregnancy
is closed. However, the future mother in any case is under the
supervision of her attending physician before the birth begins.
This is necessary to ensure the safety of both the pregnant woman
herself and her future baby. She is recommended to undergo at
least two procedures in the hospital mode for the entire period of
pregnancy.
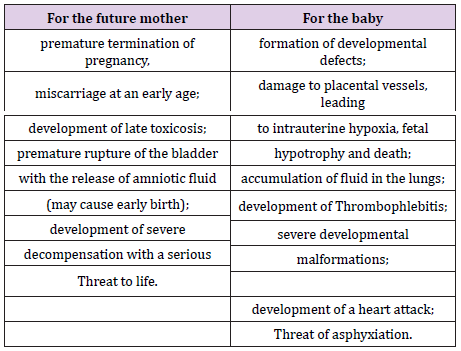
Complications
What is the risk of rheumatism in pregnancy?
In the early stages of aggravation of rheumatism can cause
miscarriage or defects in the formation of the fetus. In the second
and third trimester, exacerbation of rheumatism can lead to the
following complications and consequences [13]: damage to the
blood vessels of the placenta causes hypoxia, hypotrophy and
intrauterine fetal death;.
a) Edema and pulmonary infarction; Thrombophlebitis;
b) Rheumatic carditis of the future mother becomes the
cause of fetal hypoxia, which entails various violations of its
intrauterine development
c) Severe fetal malformations;
d) Premature separation of amniotic fluid;
e) Threat of premature termination of pregnancy; late
toxicosis (gestosis);
f) Threat of fetal asphyxia;
g) Decomposition, threatening the life of a pregnant woman.
Due to active rheumatic endocarditic, in some cases sudden
death may occur during childbirth or soon after (Table 1).
Table 1: Possible complications of rheumatism during pregnancy.
Treatment
What to do in case of an exacerbation of rheumatism and
how to cure it during pregnancy?
A. Treatment of pregnant women will depend on the
following factors:
a) The degree of the disease;
b) Clinical form of rheumatism;
c) Individual characteristics;
d) Condition of the heart muscle, valvular heart apparatus
e) Results of the survey;
f) Presence of other diseases;
g) The course of the pregnancy process.
To treat rheumatism during pregnancy is necessary, as
dangerous complications threatening the life of the future
mother and her child can develop.
B. There are several important rules in treatment [14]
a) At detection of foci of infection or expressed activity of
pathological processes (2nd or 3rd degree of rheumatism)
antibacterial therapy is shown, including the use of drugs from
the penicillin group and its synthetic derivatives.
b) In the first 10 weeks of gestation, the use of aspirin is
contraindicated because of teratogenic effects. Do not take
it before birth, because it has hypo coagulant properties and
increases the risk of bleeding.
c) In severe toxicosis, analgin cannot be used because it can
cause difficulties in removing the fluid from the body. NSAIDs
are also contraindicated, and corticosteroids are resolved only
after the end of the first trimester, when antirheumatic therapy
does not help.
Timely begun therapy in most cases saves the life of the mother
and the future baby. In the therapy of any disease, the spirit mood
is important. Often, pregnant women become depressed after
learning about rheumatism and its consequences. This is extremely
untrue. It is necessary to assess together with the doctor all possible
outcomes of the pathology and make the right choice. When there is
a real threat to the baby and his mother, it makes sense to interrupt
the pregnancy in order to undergo a full course of treatment and start
planning a re-conception. In the absence of a significant threat,
you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations and adjust to
the best. This will help the body to regain strength and coupled
with competent therapy to stop the progression of the disease.
C. What can the patient do?: The occurrence of the above
symptoms should be alerted, you should immediately contact
a therapist or rheumatologist. It is better to carry out the
treatment even before the onset of pregnancy, since medications
negatively affect the intrauterine development of the baby. In
case of rheumatism it is advisable to be treated at least twice
during the pregnancy period in a hospital. It is necessary to
comply with bed rest during the exacerbation stage, to fully eat
and fulfill all the prescriptions of the doctor.
D. What does the doctor do?: After examination, the doctor
prescribes antibiotics, drugs with hyposensitizing and antiinflammatory
action, sedatives, vitamin remedies, etc. It is
also important to monitor the condition of the baby. If future
mothers are late, you should visit your gynecologist regularly
and listen to the fetal heartbeat.
Prevention
A. Is it possible to prevent the onset of rheumatism or its
aggravation during pregnancy?
a) the risk can be minimized if one adheres to the following
principles: beware of acute infectious catarrhal diseases - avoid
public places during epidemics;
b) timely treatment of tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis, sinusitis
- foci of streptococcal infection;
c) conduct hygiene of the oral cavity - treat tooth decay,
periodontal disease, gingivitis, candidiasis of the oral mucosa;
d) do not overcool and do not undergo excessive sun
exposure; maintain immunity;
e) Ensure that the diet contains all the necessary vitamins
and microelements, the need for which is increased during
pregnancy.
B. The likelihood of developing rheumatism or
exacerbations during childbearing can be minimized by
performing the following preventive measures [15]
a) it is necessary to beware of catarrhal diseases: avoid
crowded public places during epidemics, take a complex of
vitamins and minerals for pregnant women;
b) timely treatment of foci of streptococcal infection -
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis and otitis;
c) maintain oral hygiene: brush your teeth daily and treat
dental diseases - dental caries, periodontal disease, candidiasis
and gingivitis;
d) Do not overcool and avoid long exposure to direct sunlight.
It is necessary to eat fully, walk more, avoid overstrain of
muscles, agitation and stress. It is useful to do morning exercises
and go swimming. Rheumatism in most pregnant women often
occurs before the onset of conception. The period of bearing of the
baby aggravates its course, causing a vivid clinic of the disease. This
refers to the first months when the body adapts to a new status, and
the immune system weakens [16]. As a result, control of the disease
is lost, and its symptoms are aggravated, which is a significant
threat to the baby and his mother. To reduce the likelihood of all
risks to a minimum, it is strongly recommended that you plan your
pregnancy and take timely therapy for rheumatism. In this case,
you can successfully take a future child and become a mother.
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Gynaecology Please Click on Below Link:
https://lupinepublishers-gynecology.blogspot.com/