Lupine Publishers | Journal of Urology & Nephrology
Abstract
Introduction: Amongst all of the medications prescribed to BPH patients undergoing conservative therapy, α1-blockers were used in 80% of cases. The question of optimal treatment length is one that has been constantly asked during the last years. The current study will encompass the data we have collected of a small study group of BPH patients treated with 10 mg of Alfuzosin daily, over a period of more than 7 years.
Material and Methods: From 2009 to 2011, 41 patients with mean age 67.7 years began medical therapy taking 10 mg of Alfuzosin per day. The mean treatment length was 7.6 years as of today. 16 patients (39%) with prostates exceeding 60 cm3 were additionally prescribed 5-ARIs.
Results: Overall, a positive dynamic was found in 85.4% of patients. Not a single patient chose to discontinue treatment. A very high level of satisfaction was reported by 88% of our patients. A statistically significant (P < 0.05) decrease in IPSS scores by 8.5 ± 6.1 (47.5%) was found. Mean QoL indices decreased from 3.7 ± 1.1 to 2.3 ± 1.1 over the period of observation. Mean Qmax values increased from 9.7 ± 0.52 mL/s to 14 ± 0.60 mL/s (an increase of 44.3%).
Conclusions: This study has demonstrated a high level of safety and efficacy when using Alfuzosin to treat voiding dysfunction in patients suffering from LUTS/BPH. Our study resolves the issue surrounding a prolonged course of α1-blockers, which, due to its widespread use, remains the gold standard for medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Keywords: LUTS, BPH, Alfuzosin, BOO
Introduction
It is well known that the prevalence of voiding dysfunction and patient age are in direct proportion and that prevalence is particularly high in patients over 50 years of age. Typical complaints associated with voiding dysfunction are termed lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and have a wide variety of underlying causes. The most common aetiologies of LUTS are prostatitis, urethral strictures, cystitis, bladder stones, prostate cancer, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
BPH is usually managed with surgical intervention, pharmacotherapy, or a strategy of watchful waiting, and numerous factors affect the decision of which method should be employed. Symptom severity is one of the most important subjective factors and is measured using the international prostate symptom score (IPSS) questionnaire. The nature of the symptoms (whether they fall under the category of obstructive or irritative) also influences the final decision. The primary objective factor can be considered to be the quality of voiding as measured by uroflowmetry, the interpretation of which should consist not only of the peak flow rate (Qmax), but also flow time, time to Qmax and many other indicators. Postvoid residual urine is an equally important value because it helps identify poor bladder contraction ability (detrusor underactivity) in the case of progressive intravesical obstruction. There are also those factors, no less important than both uroflowmetry and IPSS, which relate to the potential risk of BPH progression, and thus make their impact on the choice of treatment. Whilst the size of the prostate itself cannot be ignored, it is by no means a marker for surgical intervention when considered by itself, but rather a hallmark for potential future complications such as acute urinary retention (AUR) amongst other things. In recent years, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels have also become associated with BPH progression. Today, PSA levels are not only used to screen for prostate cancer, but also to reflect cellular proliferation rates of the prostate. Thus, high PSA levels increase the risk of rapid BPH progression. [1] The sum of the factors mentioned above influences the ultimate decision of which type of treatment should be employed in a specific patient.
Modern standards of medical practice dictate that pharmacotherapy is recommended in BPH patients with moderate LUTS without upper urinary tract complications, patients without obvious surgical indications, and patients who either decline surgical intervention, or are unable to commit to surgery in the nearby future. Watchful waiting is acceptable if a patient exhibits mild LUTS (IPSS ≤ 8), or if the patient’s symptoms do not significantly impact their quality of life (QoL). Patients who fall under this category should be made aware of the necessity to maintain an appropriate lifestyle as well as the importance of regular blood, urine, PSA, uroflowmetry and ultrasound testing. Surgical intervention is needed if a patient exhibits severe symptoms with upper urinary tract complications, or if there are sufficient reasons to suspect that medication will be ineffective[2,8].
In order to better illustrate modern tendencies in the treatment of BPH, we turn our attention to the TRIUMPH study. The TRIUMPH study recorded the treatment and outcomes of 2351 newly presenting LUTS/BPH patients in 6 European countries over a 1-year follow-up period. Out of the entire study population, 23.8% were managed with watchful waiting, 72.5% were prescribed medication, and only 2.7% underwent surgical treatment. These statistics accurately reflect the rise in medical management of LUTS as well as the decreasing need for surgical intervention during the past decade. It should be interesting to note that amongst all of the medications prescribed to BPH patients undergoing conservative therapy, α1-adrenergic receptor antagonists (α1-blockers) were used in 80% of cases [3].
The efficacy of α1-blockers in patients with BPH has been well documented in a large quantity of double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.[4,5,6,7] If it is possible to consider transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) the method of choice for surgical intervention in BPH patients, then α1-blockers will fall under the same criterion for the medical management of BPH. It is important to note that the European Association of Urology considers α1-blockers the first line of therapy for the management of voiding dysfunction in patients suffering from BPH[8].
Whereas the rationale behind α1-blockers does not arouse suspicion in the majority of specialists, the question of optimal treatment length is one that has been constantly asked during the last 6 years. Solutions offered to address this problem range from a life-long course of medication, to one that only lasts a few months. There is no one correct way to approach this matter, but it is the duty of every qualified specialist to incorporate certain principles when making such a decision. Personal experience and knowledge gained from a wide variety of international studies should encompass the core of such precepts. It is arguable that the lack of a formulated strategy that applies to such clinical trials is hindering the formation of a unified point of view. If we turn to medical literature, we find that despite an abundance of studies indicating the effectiveness of α1-blockers in BPH patients, the studies lack the duration necessary to examine long-term effects and are mostly comprised of 3-6 month trials with only a few mentioning 1-3 year-long results. This has led many to assume that a 3-month course (being the most prominent study length) of α1-blockers is sufficient, whilst the actual reasoning behind the short length of most studies lies in the knowledge that the results achieved during that period of time will continue over the remaining course of treatment, however long it may be. Confirmation of this can only be found in a few currently available publications that demonstrate long-term results. Most articles cite results that were obtained using studies based on principles of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) in which the categories of patient inclusion/exclusion were so rigid, they created unrealistic expectations for the wide variety of patients that are actually treated. Only a few trials provide us with results that are based on a realistic study population. Such trials include those of Roehrborn C. et al., Elhilali M. et al. 2006 and Vallancien G. with Emberton M. et al. 2008[9,10,11].
During the early 21st century, the suitability of α1-blockers was no longer debated in the Russian Federation, whilst the question of long-term use was left unanswered even for us. Even now, considering the ageing population and the necessity of prolonged medical treatment, many specialists are hesitant to prescribe α1-blockers for more than a few years without consulting medical literature about the safety and efficacy of such a treatment.
Materialand Methods
The current study will encompass the data we have collected of
a small study group of BPH patients treated with 10 mg of Alfuzosin
daily, over a period of more than 7 years. We must mention that
the data provided isn’t final, in the sense that patients are still
undergoing treatment to this day. We had not originally planned for
this to be a study with a specific design, but retrospective aspects
make it similar to various non-comparative, real-life surveillance
studies. Our goal is to introduce the reader to the results of a
longterm
course of α1-blockers that, in our opinion, are a safe and
effective method of long-term medical therapy in patients suffering
from BPH.
From 2000 to 2002, 41 patients with mean age 67.7 years (range
51– 83) began medical therapy. The mean treatment length was
7.6 years as of today. We would like to mention that this group of
patients wasn’t specifically chosen as a study group at the time, nor
were they the only patients that had been prescribed Alfuzosin. Our
detailed observation of the isolated group in question is partially
due to chance, and partially due to loss to follow-up. Patients began
treatment taking 5 mg of Alfuzosin twice daily. From January 2005
onwards, all patients take 10 mg of Alfuzosin once daily at night
due to numerous complaints of increased voiding problems during
this time. Prostate volumes fluctuated between 25 cm3 and 100
cm3, and 16 patients (39%) with prostates exceeding 60 cm3 were
additionally prescribed 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs).
During the early stages of treatment these patients were prescribed
Finasteride, but during the last 2 years many have switched to
Dutasteride in accordance with our recommendations.
Indications
Patients with LUTS/BPH
Contraindications
Patients with surgical indications
Patients known to have insufficient results from taking α1-
blockers in the past
Patients with postural hypotension
Patients taking alternative medication for LUTS with good
results
Patients with unstable angina (pectoris)
Patients with life-threatening comorbidities
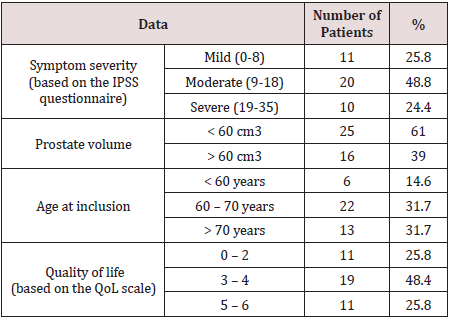
The mean duration of morbidity at the time of patient inclusion
in the trial was 1.9±1.1 years. During ultrasound testing, 31.2% of
patients had postvoid residual urine measuring 82 ± 41.7 mL. Mean
PSA levels of all patients before the trial were 2.9 ± 2.8 ng/mL. The
initial data of the patients included in this trial are summarized in
Table 1.
Out of the 41 patients, 14 (34.1%) had hypertension 11 of
which (26.8%) were receiving some form of hypotensive therapy,
and 5 patients had suffered a myocardial infarction before inclusion
into the trial.
The efficacy of the treatment was analysed using IPSS scores as
well as QoL indices. Additional factors included Qmax and prostate
volume in patients who were receiving combination therapy with
5-ARIs. The safety of the treatment was analyzed based on recorded
incidents of adverse cardiac side effects (mainly hypotensive)
during the trial. Vital-sign dynamics were also analyzed. Follow-ups
were conducted biannually during the first 2 years, and no less than
annually thereafter.
Two-sided hypothesis tests were conducted with a significance
P-value cut-off of 0.05. Dynamics of safety and efficacy variables
were analysed before and after the trial (absolute and relative
change was considered). A paired Student’s t-test was used if
statistics followed a normal distribution; a Wilkinson’s test was
used if they did not.
Results
Not a single patient chose to discontinue treatment, notwithstanding the long period of observation. We must mention, however, that several patients stopped being prescribed Alfuzosin during the early stages of the trial but were obviously not considered in the study group. Subjective assessments of patient satisfaction were carried out using a questionnaire specifically tailored to this publication and not used in our routine clinical practice. A very high level of satisfaction was reported by 88% of our patients, whilst the remaining 12% consisted of those actively taking a large quantity of medication for various comorbidities, and patients with diabetes. Many of the aforementioned patients were prescribed medication after they began treatment with Alfuzosin. Therefore, these facts could be taken into consideration by general practitioners who have patients undergoing treatment for LUTS.
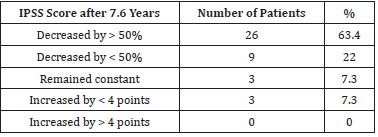
Mean IPSS scores were 17.9 ± 5.3 before the treatment, and 9.4
± 5.2 after 7.6 years. A statistically significant (P < 0.05) decrease
in IPSS scores by 8.5 ± 6.1 (47.5%) was found. A decrease in IPSS
scores by > 50% was noted in 28 patients (68.3%). Overall, a positive
dynamic was found in 85.4% of patients. IPSS score dynamics are
summarized in Table 2.
Dynamics of irritative (questions 1, 3, 5 and 6 on the IPSS
questionnaire) and obstructive (questions 2, 4 and 7 on the IPSS
questionnaire) symptoms were also analyzed. Mean irritative IPSS
scores decreased from 6.3 ± 2.9 to 3.7 ± 2.4 (33.7% lower) whilst
mean obstructive IPSS scores decreased from 9.6 ± 4 to 5.5 ± 3.7
(35.7% lower). Incidents of nocturia decreased from 2.4 ± 1.1 to 1.5
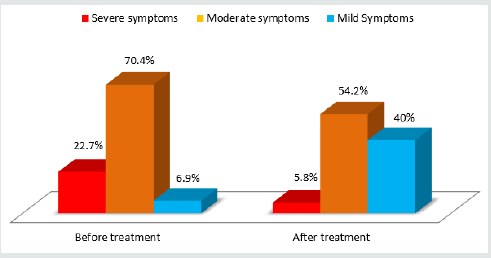
± 1.1. Diagram 1 illustrates a major decrease in the percentage of
patients with moderate to severe voiding dysfunction symptoms as
well as a six-fold increase of patients with mild symptoms. All of the
statistics mentioned above were statistically significant (Figure 1).
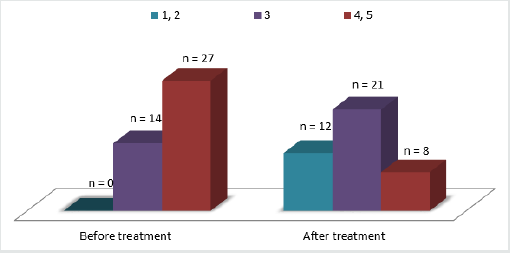
QoL dynamics are presented in diagram 2. Mean QoL indices decreased from 3.7 ± 1.1 to 2.3 ± 1.1 over the period of observation. The mean decrease in QoL indices was 32.3% (reflecting an increase in QoL). All changes were statistically significant. Overall, 72.7% of patients had an increase in their QoL (Figure 2).
It is important to note that the minority of patients who did not demonstrate clear improvements in symptom severity either underwent surgery or continued to take Alfuzosin. The latter group either demonstrated a minimal but satisfactory improvement or was unable to undergo surgery for various reasons. We believe that it is of utmost importance to understand that the current publication presents a comparative analysis before and after Alfuzosin treatment, and whilst all of the patients had demonstrated an improvement during various periods in the trial, the dynamics of IPSS scores and changes in QoL were not registered at those intervals. It is also important to highlight the role of the detrusor in BPH symptoms, something that was originally demonstrated by Russian authors O.B.Loran and E.L.Vishnevskiy in 1998. The contraction capability, level of energy metabolism, and nature of the biochemical events of the detrusor influence voiding quality no less than the level of intravesical obstruction.[13] This could explain treatment ineffectiveness in certain patients.
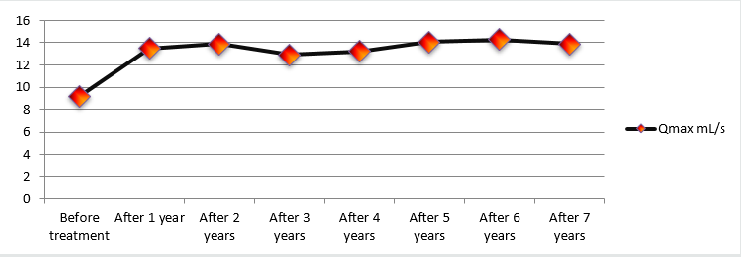
Changes in Qmax over the course of the study were considered as a secondary measurement of treatment effectiveness and were analysed during every follow-up, making this particular variable very intriguing. Mean Qmax values increased from 9.7 ± 0.52 mL/s to 14 ± 0.60 mL/s (an increase of 44.3%). Diagram 3 illustrates Qmax dynamics throughout the entire length of the study. One can conclude that early treatment results remained constant throughout the observation period (Figure 3).
During the period of observation, 5 patients underwent TURP
procedures. The rationale behind TURP in one patient was due to
an episode of AUR provoked by alcohol ingestion. After 3 days of
catheterisation, the patient did not show any signs of improvement
in voiding ability and was subsequently operated. The other 4
patients exhibited worsening LUTS as shown by an increase in
their IPSS scores. During ultrasound and transrectal ultrasound
testing, a median lobe was detected in all 4 patients. All operations
performed did not deviate from a standard TURP procedure.
The median prostate volume of the 16 patients receiving
combination therapy had decreased. The value fell from 74.1 cm3
before treatment to 50.1 cm3 after 7.6 years of therapy (a decrease
of 32.4%).
Throughout the trial, PSA levels of all patients were measured
annually. Median PSA levels were 2.9 ng/mL before the trial and
3.2 ng/mL afterwards, demonstrating no significant variance. PSA
levels of patients undergoing combination therapy were considered
after the second year of treatment and were doubled. PSA levels of
over 4 ng/mL requiring transrectal ultrasound-guided multifocal
prostatic biopsies were noted in 3 patients aged 68–74 years. None
of the subsequent histological analyses revealed the presence of
cancerous cells.
The safety of this treatment was assessed based on the
frequency and type of adverse side effects recorded during the
trial. In total, 9 patients (22%) exhibited adverse effects. The most
common findings were dizziness (2 patients/4.9%) and asthenia
(2 patients/4.9%). Another 3 patients experienced dyspepsia,
shortness of breath and headaches. Out of the 16-patient subgroup
receiving combination therapy, 2 patients complained of decreased
libido (possibly attributed to 5-ARIs). One of these patients had
their sexual drive normalise after 1 year of therapy, whilst the other
retained a low libido throughout the treatment. Considering the
relatively small study population involved, a true understanding of
the statistical significance of these adverse effects as well as their
immediate connection to the treatment in question is not possible.
However, the fact that most of the aforementioned adverse effects
were present as isolated episodes in patients during the first week
of therapy demonstrates a high level of treatment safety.
Discussion
The current study has demonstrated a high level of efficacy with minimal adverse side effects in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) arising from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist (α1-blocker) Alfuzosin. The effectiveness of the treatment was determined using subjective and objective criteria. A 45.7% decrease in LUTS severity as measured by the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) questionnaire was found in 85.4% of the entire study population. Mean Quality of Life (QoL) indices measured using the QoL scale increased by 32.2% and mean peak flow rate (Qmax) values increased by 44.3%. The fact that the positive results achieved during the early months of therapy had stabilised and showed no signs of regression during the entire study period is quite remarkable. Such results verify the notion that a prolonged course of α1-blockers provides consistent long-term results. The high level of patient satisfaction with treatment results and the information that patients themselves have provided us with, mark not only the fact that patients are not bothered by the need to take medication daily, but also (and most importantly) the great sense of confidence patients feel regarding the stability of the results they have achieved, leading to a positive outlook on their future treatment.
Several observational studies indicate results very similar to
ours. In the ALFORTI study, 311 patients on Alfuzosin were surveyed
over a period of 9 months. A decrease was shown in mean IPSS
scores and QoL indices measuring 45.6% and 36.4%, respectively.
Adverse effects (most likely due to the medication in question)
occurred in 4.4% of the study population.[12] A similar study
published by the same authors analyzed the safety and efficacy
of Alfuzosin. A decrease in mean IPSS scores and QoL indices was
shown and measured 32% and 27.8%, respectively[14].
Combination therapy in the form of α1-blockers and 5-alphareductase
inhibitors (5-ARIs) is currently the recommended form of
treatment in patients with LUTS and an increased prostate volume
according to the European Association of Urology.[12] The safety
and efficacy of this treatment has been confirmed by a considerable
decrease in LUTS severity and prostate volume (a mean decrease of
32.4%) in our 16 patient subgroup. Similar results have also been
demonstrated by such well-known trials as MTOPS, ALTESS and
COMBAT[1,2,8,9].
When the information provided by the various authors is
analysed, it becomes apparent that Alfuzosin attains a similar
degree of effectiveness in every single case. The fact that the results
gained from a continuous course of therapy remain consistent
throughout prolonged treatment is extremely important, but
perhaps the most interesting observation made during our trial
is that the considerable results are not only long-lasting, but are
achieved and made stable during the first month of treatment.
A study conducted in 2008 by Vallancien G. et al. is one of the
few studies (similar to ours in design, but not in duration) that
analysed the data collected in a real-life surveillance study format
regarding the effectiveness of Alfuzosin during a 3-year course of
therapy. The results were as follows: mean IPSS scores decreased
by 33.4%, mean QoL indices by 40.7%, and nocturia severity by
25.5%. Adverse side effects (likely related to vascular dilation)
were registered in 4.5% of cases, and surgical intervention was
required in 5.7% of cases. These results are clearly similar to ours.
[10] Similar findings were also recorded earlier during the ALFONE
trial published by Elhilali M. et al. in 2006[11].
Whilst several adverse cardiac effects were noted, the analysis
of adverse side effects in our trial is far from thorough, which is
explained by the lack of the patients enrolled in the trial leading to
insufficient statistical integrity. A study involving a multidisciplinary
approach could aid the understanding of various guarantees that
we may be able to give our patients in the future. These days,
patients mostly consist of elderly men whose age and comorbidities
make the use of pharmacotherapy ideal for managing the
symptoms associated with BPH. Perhaps tomorrow, the necessity
of prescribing Alfuzosin for over 10 years will increase considering
the continually regressing number of patients who choose surgical
intervention for BPH management; those that wish to retain a good
quality of life whilst remaining ‘real men’ for many years to come.
Today, when patients inquire about the potential length of their
treatment, they are told that they may take Alfuzosin for as long as
it is required.
Conclusions
This study has demonstrated a high level of safety and efficacy when using Alfuzosin to treat voiding dysfunction in patients suffering from LUTS/BPH. Furthermore, it is important to mention that many researchers have come to the same conclusion. Our study, whilst potentially lacking in statistical magnitude, resolves the issue surrounding a prolonged course of Alfuzosin, which, due to its widespread use, remains the gold standard for medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Urology & Nephrology Please Click on Below Link:
https://lupine-publishers-urology-nephrology.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.