Lupine Publishers- Environmental and Soil Science Journal
Introduction
In recent years, both in the Republic and in the CIS and
far abroad are developing low-intensity stationary systems of
irrigation, consisting of Micro Sprinklers, impulsive actions, aerosol
auto oscillatory action sprinkling irrigation, auto oscillatory action
auto oscillatory action combined, the drip, drip pulsing and a
number of others. This is because low irrigation system has a
number of significant advantages over other methods of irrigation.
Especially promising the creation of automated sprinkling systems
impulse machines, combined, auto oscillatory action stepper
auto oscillatory action rocker type, pulse-airborne apparatus
auto oscillatory action, etc. It should be noted that these systems
allow to reduce the capital cost of their construction, also ensure
the principle as “sprinkling” or “drip” in condition of daily water
use plants. That is to create optimal conditions for the growth and
development of plants during their growing season (Figure 1).
Moves the study
Automated watering crops the basis for high yields and
productivity. Therefore, from the elements and devices used
automatics require reliable and uninterrupted operation. Therefore,
starting from the design stage through these devices and the
production and operation, reliability issues, because the problem
of reliability is not only technical, but also an important economic
task. Reliability theory developed in recent decades, offers a great
opportunity for a qualitative assessment of the reliability of existing
irrigation technique, including micro irrigation systems. Reliabilitythis
property of equipment or system to perform specified functions
to maintain their performance within the required period or time
required. From among the existing irrigation technique, stationary
sprinkling system consisting of a large number of similar elements
in a specific order on the field and required for the irrigation of crops.
Determining the reliability of one of these elements will decide the
reliability of systems. Reliability issues fixed irrigation systems in
particular, equipped with sprinkling installations engaged in many
of the scientists in the former Soviet Union and abroad. To examine
the elements of the calculation on reliability of low-intensity
sprinkling (for example pulse sprinkling auto oscillatory action)
should consider the technological feasibility and sprinkler systems.
Optimal low irrigation system parameters were determined by us
by searching for the specific functions listed minimum cost with
UD. Depending on the area of the system S; aspect ratio θ; the cost
of the system (Q); Mr pressure corresponding to the pressure
dictating point; conditional irrigation period tat equal i/q 3600
ì where,
m irrigation norm, m; q / -maximum ordinate hydro-module m/s).
Number of distribution pipelines (N); the distance between
irrigation technique (sprinkle plants) l; x factor, equal with the
placement of devices on square 0.2; the length of the i-th pipeline system l(i) its diameter (D)(i) and discharge Q(i) , the coefficients
(k), (m), β -dependent roughness of the internal the surface of the
pipes; costs of irrigation Engineering (sprinkler devices, etc.). With
g and the pressure Sn site; the cost of one kW/h of electricity; ψ,
coefficient η pump unit equal to 0.7 coefficient of non-uniformity
of flow
gde, r- ratio splash start P2 to pressure end splash r1), equal to
1.02-1.25; factor e0 = e1 +e2 (e1, e2 -regulatory factors of efficiency
of capital investments and annual deductions for depreciation and
repairs); coefficients (b), (d) dependent on the material and the
cost of pipe laying and operating costs of the attendants e(n): [1,2]
Studies have shown that the most economical option is the
simultaneous operation of all sprinkler devices system, i.e., when
the system is produced by the limit dispersal of current irrigation
[3] in this case has a minimum at points determined by the
expressions:
Where is
Substituting in the formula (3) and (4) coefficients
corresponding to steel pipelines (d = 1.4; m = 5.1; β= 1.8; K =
0.00107; In = 50; E0 = 0.2; Ton = 1.1), obtain payment formula to
determine and that for ease of use, represented by nomogram
(Figure 2). Similar monograms built and for pipes made of plastics
and other materials. Optimal pipeline diameters (D)opt, I, number
of irrigation pipelines x, suspended from the distribution pipeline,
number of sprinkler devices on the polynom pipeline y define the
following ratios:
If you change the original parameters S, q/, θ, m) within: < = 30
S < = 300 ha, 10 0.3-7 < = q/ < = 1.0 x 10-7 m/s, < 0.25 = θ < = 4, 0.3
< = M < = 1.0 m
1000 m3/HA, the optimal system settings change within: 35 < =
l < = 135 m; 3 < = N < = 65; 1 = < x < = 50; and 1 < = y< = 33. Being
attached to squares, laid down specific natural-economic conditions
define systems parameters of irrigation on low-intensity pulsed
example sprinkling [4]. Consider these square set and equal to 150-
400 ha and have an average optimal relationship of the parties 1-3
and natural-economic conditions irrigation norm 0.35-0.75 m and
a maximum ordinate 0.6 x 10 hydro-module-7 -1.0 x 10-7 m/s.
Averaged source data S= 200 ha, θ = 2; M = 0.55 m, q/ = 0.8
x-7 m/s, the following optimal system settings l= 50m, N= 22, x =
10, y = 8 obtained using the following programs and formulas
(4.5). For other crops and natural-economic conditions these
parameters are defined similarly. Obtained values of N, l, x, y, (D)
opt. I -enable you to define the basic construction and
technological
parameters of irrigation equipment (impulse sprinklers apparatus
self-oscillating action): as head n2, corresponding pressure start
splash RV2, head n1, the pressure end splash r1; constructive
volume pneumatic accumulator W0 and nozzle diameter (D) [3,5].
Based on the submissions of works of scientists of the world, and the
results of Erosion and irrigation in the Institute research on
some definition NANA parameters of irrigation technology in
conventional machines, sprinkler machines pulse actions, etc., for
which we offer the following characteristic control to determine
the basic parameters of pulse devices depending on pressure. But
corresponding to the initial pressure pneumatic accumulator p0
and the corresponding atmospheric pressure p and cross -sectional
areas, bringing the pipeline ω2 inlet flow coefficients pneumatic
accumulator μ1 and μ nozzles2, resources pneumatic accumulator t*,
sprinkler apparatus N*, the coefficients that depend on the value of
sprinkler apparatus (d)1 and (d)2, [1,2,3,7].
It should be noted that equation (6) matches the water supply
and water plants, and equation (7) and (8), respectively, the
optimum size of sprinkler devices and agro technical requirements
and quality of rain (the number of sprinklers drops with a diameter
of more than 1.0-1.5 mm in overall flow rain Jet should be less than
10%). Each group of m, q, S, θ correspond definite values x, y, N, l and
system settings h2 n1, W0, D pulse settings of the apparatus. Bearing
in mind that the real system tM1 = t >M2 and sum of hydraulic resistance
to worst according to the terms of the pnevmogidroakkumljatora
filling system Σ ξ = > 1, equation (6) you can submit in the form:
[1,7]
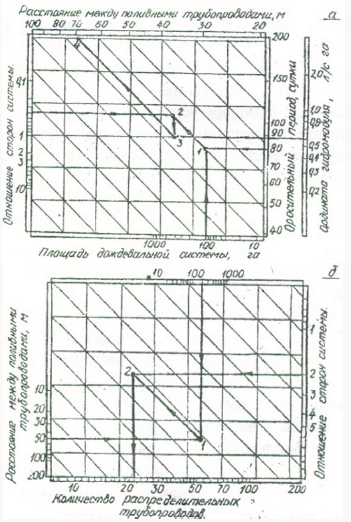
Qi-factor of 2.64 for steel pipes. 10-3/Equation (7,8 and 9)
together with the formula for Ap Ruseckogo represent a closed
system of equations. The below Figure 2 provides a graphical
solution of this system. Knowing the economic radius of action
impulse apparatus and setting from system (= 3-5), the search for a
solution should lead to corresponding with curves in the following
order and1 and4, and7 and10 for s = 3, by and 2 and5 and8 and11 when
c =4 and3 and6 and9 and12 when c =5. Parameters of sprinkler unit with
intermediate values with determined by interpolation. Using the
results obtained previously, define the structural and technological
parameters of pulse apparatus for the same natural-economic
conditions. With the placement of devices on the squares economy
its radius R= 21-35, and c = 3 [1,3]. Using monographs s and the
input values to and (C) pulse parameters are as follows:
(P)1= 450 kPa, P2 = 700 kPa, W0 = 0.19 m3, D= 20 mm.
To address the complex of actions on system reliability is
reliability elements sprinkler systems. Research of reliability
indicators of basic elements of fixed sprinkler system are the
results of theoretical and experimental research, evaluated, tele
control devices noise immunity parameters dispersion, irrigation
norms precipitate individual sprinkling and installed types and
parameters of distributions of operating time to failure of the main
elements of the systems sprinkling [3,4]. In moments the adoption
of tele control device command “select object” in the network of
technological pipelines occur transients. Found that the pressure
p can be set to lower static pressure reconfiguring tele control
devices r/
0 and duration of exposure of the false signal can reach
0.15-1.2 sec. Received the following experimentally confirmed the
dependence between team processing time signal tk , swing Rod
h effective membrane area (F)e, a cross section of tube connecting
the technological pipeline with working hydraulic factor ω dental
rigidity to the recoil spring2 , specific gravity γ water b and the
acceleration of gravity (g) :
According to the formula (10) evaluated the time reconfiguring
device automated tele control. At instant slide. pressure in the
hydraulic drive to atmospheric pressure, kPa, corresponding
pressure 340 item Chooser requires 0.34 c 1.5 times greater than
the duration of a false signal. (10) allows you to not only assess the
time reconfiguring devices of automated process control systems
tele control channel irrigation, but to appoint him constructive
value parameters in accordance with the requirements of noise
items tele control systems [3]
Start pressure dissipation of impulsive actions self-oscillatory
apparatuses splash leads to dispersion of their volumes Δ splash W
layer and therefore rain m, so how are they related dependencies.
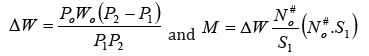
(the number of cycles of performance in a year and its service
area). Testing of pulse (100 picks) and the subsequent processing
of the received data found that distribution of r2 and r1, subject to
the normal law with coefficients of variation of νP2 = 0.04 and νP1 =
0.093. Bearing in mind
A what
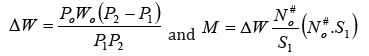
the density distribution of m can be represented as:
from constructive impulse imperfections. Obviously, the smaller
the ratio δΔw/Δ W , the machine better.
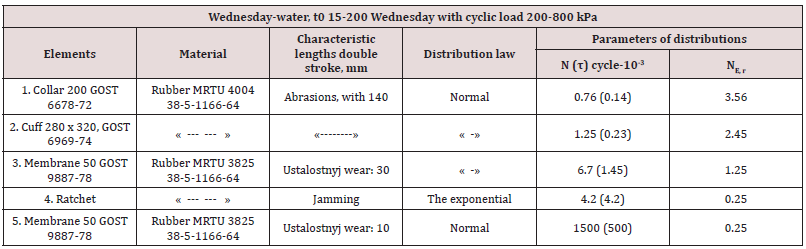
Studies (Table 1) on the definition of the types and distributions
of operating time to failure ( N , σ- coverage and root mean square
deviation) typical sprinkling systems devices, including the most
common elements in hydro automatics: the underground sliding
hydrants (elements 1, 2), devices, systems automated supervisory
control (items 3, 4), yaw (element 5) as well as impulse sprinkler
machines (6.7 items, 8, 9). It is established that the distribution of
time to restore those elements, you can characterize the average
recovery time tin [3,6].
Discussion of research results
As a result of special research received the following relationship
between the average service life of parts made of rubber or plastic
tWed, the average number of cycles N#
0 a year and experimental aging
value of these materials in the water t0equal to 6.8 years:
In addition to these activities required to address the optimal
level of operational reliability of stationary systems should
develop institutional arrangements. For organizational activities
of particular importance was the implementation of preventive
works and correctly spent time. The timing of prevention is one
of the main problems of preventive maintenance, which is closely
linked to the content of preventive works and the Organization of
their execution [7]. These terms are usually defined in the study the
following objective function:
where, with1,2 respectively, the cost of replacement of parts
when troubleshooting failures and preventive replacements; (M)
(t), N(t)-respectively, the average number of replacements in case
of failure and preventive services for time t.
Scientific conclusions
Expelled us measure perfection is appropriate with a view to
selecting the best design because it is economically summarizing
indicators of maintainability of systems security, persistence, and
sprinkling
Follow on Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/lupinepublishers
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online

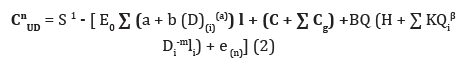
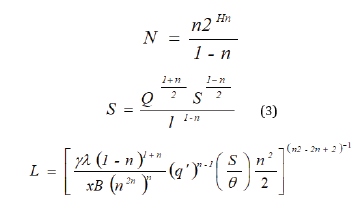
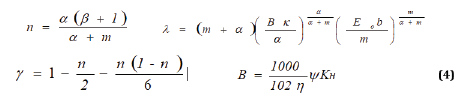
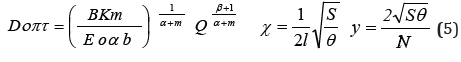
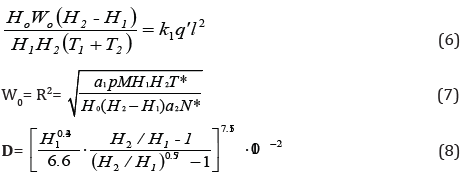
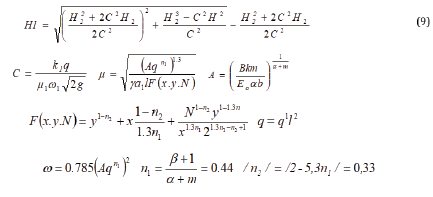
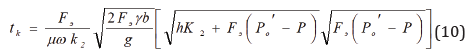

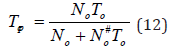

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.