Background
Globally, including the United States, cigarette smoking is the
single most important cause of premature death, even though it is
preventable. The prevalence of smoking is high, although some resources
have been dedicated to this problem. A variety of interventions have
been tried on smoking prevention. From the public health perspective, it
is the biggest concern. As there are numerous health benefits of
smoking cessation, most individuals who smoke express a desire to quit.
Studies show that most smokers in the United States and the United
Kingdom report that they want to stop or intend to leave smoking at some
point in life Hyland [1]. A multitude of non-pharmacological and
pharmacological interventions now exist to aid smokers in cessation.
Objectives
To bring awareness among public and policy makers. To provide
evidence and recommendations required for effective cessation
interventions. To be carried out in public health globally.
Methods
Articles published from 2000 to 2016 were identified through electronic databases such as Medline, Pub Med, and EBSCO host.
Conclusions
This research paper suggests the trends of smoking habits and smoking
cessation intervention strategies differ from region to region when
viewed from an international perspective. This highlights the necessity
for the improvement of new methods that prevent people from starting to
smoke, motivate smokers to quit and enable them to sustain long-term
cessation. Future research should examine whether increasing the rate of
quit attempts would be key to improving the population smoking
cessation rate.
Keywords: Smoking Prevention; Tobacco Use; Smoking Cessation; International.
Introduction
This article is a retrospective review of research articles on
smoking cessation obtained through a search of selected databases from 1
Aug 2017 back to 31 Dec 2000. The purpose and goal of this report is to
bring awareness to the population. Additionally, to provide data for
professionals in public health and policymakers, to help make
recommendations based on effective cessation intervention evidence.
Also, to provide information to youth who indulge in tobacco smoking of
the trends, prevalence, consequences and to inspire engaging in programs
for smoking cessation.
Methods
The articles published from 2000 to 2017 were identified
retrospectively through electronic databases such as Medline, Pub Med,
and EBSCO host. Peer review articles relevant to smoking cessation were
chosen. Statistical information was gathered and further analyzed.
Besides web-based resources, other important resources such as the
Center for Disease Control (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO)
were also utilized for research.
Background
Even though several preventive measures have been taken by the
governments and several organizations, smoking remains a constant and
severe problem in communities all over the world. Smoking-related
diseases claim an estimated six million lives each year out of which
600,000 deaths were from exposure to second-hand smoke, though it is
entirely preventable (WHO, 2014). An estimated 126 million Americans are
regularly exposed to secondhand smoke each year National Institute on
Drug Abuse [2]. More than 43 million adults are current smokers in the
USA. Eighty- eight percent of those adults who started smoking at their
youth (age 11-12 years) almost became an addict when they turned 14.
Globally, as well as in the.com, tobacco smoking has been the leading
cause of preventable death. The prevalence of youth smoking is high,
although some resources have been dedicated to this problem and the
variety of interventions that have been tried to prevent smoking is a
big concern from a public health perspective. As there are numerous
health benefits of smoking cessation, most individuals who smoke express
a desire to quit smoking. Studies show that the majority of smokers in
the United States and the United Kingdom report that they want to stop
or intend to quit smoking at some point in life.
In India, tobacco's associated mortality is the highest in the world,
an estimated 700,000 annual deaths attributable to tobacco use Murthy
[3]. Whereas, the lowest smoking rates for men can be found in Nigeria,
Barbuda, and Antigua. For women, smoking rates are lowest in Eritrea,
Cameroon, and Morocco (UW TODAY, 2014). A multitude of
non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions now exist to aid
smokers in cessation. The financial burden imposed by cigarette smoking
is enormous. Smoking- related illness in the United States costs $96
billion each year in medical expenses and $97 billion in lost
productivity due to premature mortality. Cigarette industries are
spending billions of dollars on advertising tobacco products, attracting
specifically adolescents and young adults who fuel the existing burden.
The primary cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and
lung cancer in adults has been cigarette smoking. There is an
association between smoking and periodontal disease in children and
adolescents. Smoking is responsible for 87% of the lung cancer deaths in
the United States. It is responsible for 30% of all cancer deaths
universally. Cigarette smokers have a lower level of lung function than
those persons who have never smoked. Smoking hurts young people's
physical fitness regarding both performance and endurance, even among
young people trained in competitive running. On average, a person
smoking a pack or more of cigarettes per day lives seven years less than
the person who never smoked (Department of Health & CDC, 2008). In
2007, 1,800 Hispanic women and almost 3,000 Hispanic men died of lung
cancer. Cigarette smokers are also known to possess a greater risk than
nonsmokers for heart attack (in the same year, about 3,000 Hispanic
women and nearly 3,800 men died from heart attack.Smokers have a 70%
greater chance of dying from coronary heart disease than non-smokers
(Department of Health & CDC, 2011).
Overall, lung cancer is known to be the leading cause of cancer
deaths among African Americans. Multiple factors are associated with
tobacco use such as social, physical and environmental. Young people are
more likely to use tobacco if their peers use tobacco. Perceived
smoking is acceptable or normative among their peers. They expect
positive outcomes from smoking, such as surviving with stress, anxiety,
and depression. Parental and sibling smoking may also promote smoking
among children and youth in a household where perceived parental
approval plays a significant role in adolescent smoking. In Hispanic and
Asian communities, families live intimately with each other. Parents
have control over their children and watch their activities, and vice
versa offspring also respect parents and elders. Hispanic youth are more
likely than other young people to be protected from second-hand smoke
by smoking bans at home. Seventy-one percent of Hispanic households do
not allow smoking in their homes. Parenteral perceived disapproval of
smoking is a protective factor against adolescent smoking McCausland
[4]. Other factors like low socioeconomic status, lack of parental
support or involvement, accessibility, availability, low level of
academic achievement, low self-image and aggressive behavior have been
associated with youth smoking Miller [5]. Peer pressure is a significant
factor in their decisionmaking process. There are many studies showing
that the influence of peers is especially powerful in determining when
and how young people first try a cigarette. Even if someone thinks that
their child is too smart, all children and adolescents are vulnerable
either for negative or positive influence. Kids feel that they are
pulled in two directions-on the one hand they do not want to use tobacco
but the other side they afraid of losing friends. The smoking rate
among children and young adults who have three or more friends who smoke
are ten times higher than those who report that none of their friends'
smoke Nicotine & Tobacco Research [6].
According to a study concerning accessibility of cigarettes, it is
seen that among the 12.9 percent of students nationwide who tried to buy
cigarettes 30 days before the study, 48.5 percent them were not asked
to show proof of age. The prevalence of students, not having been ID'd
to show evidence of age was higher among ninth graders at 70.4% than
tenth graders at 55.6%, eleventh graders at 59.2%, and least for twelfth
graders at 32.7%. For females, it was higher among eleventh graders at
57.7% compared to twelfth grader females at 29.3%. Among males,
ninth-graders were at 65.7%, tenth graders were at 55.6%, eleventh
graders were at 59.6% and finally twelfth graders at 34.9%. Illiteracy
is another factor in youth smoking. According to the.com Census Bureau
report from 2007, 61% of Hispanics in comparison to 85% of non-Hispanics
have a high school diploma. While only 12.5% of Hispanics compared to
30.5% of non-Hispanic, have a bachelor’s degree (NSDUH 2010) [7].
Currently, there is an increasing trend of smoking prevalence among
young women, low socio-economic, racial/ethnic minorities, and
vulnerable populations such as the LGBT community (lesbian, gay
bisexual, and transgendered) (USDHS, 2004). As regards quitting smoking,
a study shows that Hispanic smokers are less likely than white smokers
to be prescribed or to attempt quitting (CDC, 2016) (Table 1, 2).
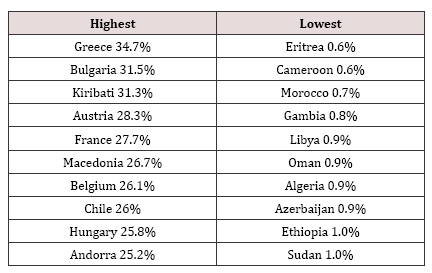
Table 1: Countries that had the highest and lowest smoking prevalence for men in 2012.
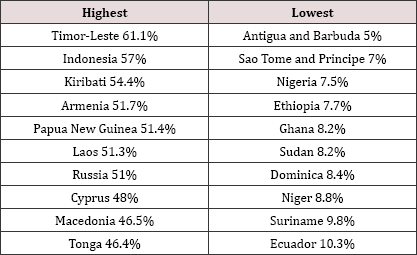
Table 2: Countries that had the highest and lowest smoking prevalence for women in 2012.
Health impact
Secondhand smoke exposure puts family members of smokers at an
increased risk. The following table illustrates the various health
impacts in children and adults:
Other benefits of quitting smoking are reduced chances of impotence,
having difficulty getting pregnant, having premature births, babies with
low birth weight and miscarriage. In children, the risk factors of many
second hand smoking such as asthma and other respiratory diseases
decrease Stead [8]. After quitting smoking, there are numerous physical
and emotional effects the body experiences. These effects consist of are
both short-term and long-term benefits. The short term benefits, which
can commence as soon as 20 minutes past quitting, include heart rate and
blood pressure decrease. Carbon monoxide level drops to normal after 12
hours. There is an improvement in blood circulation and lung function
after two to twelve weeks of quitting. Shortness of breath and coughing
decrease after one to nine months of stopping. Subsequently, two to
three weeks following cessation, several regenerative processes begin to
take place in the body. The long-term benefits of quitting reduce the
risk of coronary heart disease after one year to one and a half. Five
years past quitting, the probability of stroke is reduced to that of a
nonsmoker. The potential for lung cancer, cancer of mouth, throat,
esophagus, bladder, cervix and pancreas reduces to about half of that
for a smoker. Within 15 years of cessation, almost all of the
recuperative processes are completed. The risk of heart disease is no
greater than someone who has never smoked a cigarette CDC [9]. The
advantages of quitting smoking compared to those who continued to smoke
are huge. Life expectancy is increased compared to those who continued
to smoke. The probability of suffering from another heart attack is
reduced by 50% for people who quit smoking after having a heart attack
or following the onset of life-threatening disease (Table 3).
Table 3: WHO, 2011.

Dependence and Relapse
The addictive effect of nicotine once smoked, makes hard to quit
smoking. Early initiation increases the likely-hood of habituation, and
continuous tobacco smoking eventually ends up in addiction. People who
begin to smoke at a very young age are more likely to develop severe
levels of smoking than those who start a later age. Tobacco addictions
should be treated as a chronic disease with a constant risk of relapse
Fiore [10]. Based on literature review, many studies have proved that
tobacco is apparently more addictive than any other substance abuse.
According to one study high rates of relapse among smoking quitters
occurs due to the addiction potential of tobacco. It is reported that
brief counseling has resulted in a quit rate of 55% the relapse rate
among quitters was 23% Warner [11]. The current improved knowledge of
the neurobiology of nicotine addiction has significant implications for
the management of its dependency Joy [12].
Challenges for quitting
There are many challenges and barriers to quitting. There are three
critical challenges that one should be acquainted with before planning
to assist smokers to quit or attempt to quit. All people do not have the
same reasons why they smoke and why they could not quit. The reasons
have been classified into three categories. Physiological addiction;
behavioral and environmental social; emotional or psychological
connections WHO [14].
Smoking Cessation, Smoking Prevention and Methods to Quit
The Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence-Clinical Practice Guideline,
issued by the United States Department of Health and Human Services,
recommends the 5A’s and 5 R’s approach that should be addressed in a
motivational counseling intervention to help those who are not ready to
quit (HHS, 2012). The below figure illustrates the motivational
counseling interventions:
There are seven first-line medications available that are known to
increase long-term smoking abstinence: Nicotine inhaler, Nicotine gum,
Bupropion SR Nicotine lozenge, Nicotine patch, Nicotine nasal spray, and
Varenicline. Current information on adolescence tobacco use prevention
has proposed that macro-level approaches can be effective in reducing
the prevalence of tobacco use among adolescents. The stronger tobacco
control policy that increased tobacco taxation and counter-marketing
campaigns has all proven to be successful strategies for reducing youth
tobacco use Backinger [14]. The use of counseling and pharmacotherapy
together has been reported as the most effective strategy to achieve
tobacco abstinence. The time spent on counseling is very effective since
it has got a significant association between the time devoted to
counseling a person quitting smoking and their chances of quitting.
According to WHO guidelines, more than one type of pharmacotherapy
should be offered in combination, if appropriate, for a prolonged
period.
After identifying and understanding different sub-groups, various
communication strategies should be developed for specific focus groups
that enhance the impact of health information. The Community Preventive
Services recommends the use of "mass- reach health communication
interventions" e.g. television and radio broadcasts, newspapers,
billboards, built on solid evidence for their advantageousness in
preventing or reducing cigarette smoking and increasing use of cessation
services like quit lines. Regarding the use of media, studies suggest
that the success of different types of smoking cessation messages may
vary by socioeconomic status, predominantly income and education status.
Cessation programs must be custom-made to focus on the envisioned
audience rather than just providing information Strickland [15] (Table
3).
Nicotine replacement therapy
Among the currently available smoking-cessation treatments, including
nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), bupropion and varenicline are
well-known pharmacological interventions to raise the chances of
quitting tobacco smoking, mainly when combined with health education and
counseling programs. Various studies have shown that tobacco cessation
assistance provided by health professionals (physicians, nurses,
dentists, pharmacists and other health care workers) enhances the quit
rate among their patients Gorin [16]. Almost all forms of NRT gum,
transversal patches, nasal sprays, inhalers and sublingual tablets can
help persons who make a quit attempt and increases their chance of
successfully quitting smoking by 50% to 70% irrespective of any setting.
The purpose of NRT is to briefly replace considerable nicotine from
cigarettes and to decrease the stimulus to smoke and avoid nicotine
withdrawal symptoms consequently to ease the transition from smoking to
complete abstinence.
Quit-lines
Quit-line is a tobacco cessation program which is a phone based
service that helps tobacco users quit smoking. Today, residents of all
50 states in U.S. and Canada, have access to quit lines services. In the
recent years, Quit-lines have been able to become a critical part of
the tobacco control efforts that are ongoing in the United States. The
universal access, demonstrated efficacy and the convenience of remote
counseling via telephone have all led to the quick and widespread
adoption of Quit lines in the North American region Cummins [17].
Currently over 53 countries have at least one national toll-free quit
line with a person available to provide quit line cessation services,
with access to its population. All the 50 states of USA and Canada are
having multiple quit lines operated by Federal government, state
government and non-governmental organizations. Out of 53 countries, 32
(60%) of them are wealthy countries and four countries (8%) are of low
income and 17 of them are middle-income countries which made up only18%
of all middle- income countries in the world, have at least one national
toll-free quit line. There is the noticeable difference in reach as
well as type, quality, quantity, volume and of services provided by
different quit lines. The counselors and supervisors working in quit
lines are well trained by the psychiatrists for operational purpose of
smoking cessation assistance. Quit-lines are established in
collaboration with health care system, health care providers,
nongovernmental organizations, and governments both local and national.
Among the primary methods used by countries to promote quit line
services are media advertisements (newspapers, television, radio or
flyers). Some countries, including Brazil, New Zealand, South Africa,
and all the European Union (EU), have printed the quit line number on
cigarette packets together with health warnings. In spite of their
widespread presence, information including international data on how
Quit-lines services operate in practice and their outcome is not readily
available Gollust.
Complementary and alternative medicine
Very few studies have been confirmed that the complementary and
alternative medicine (CAM) for tobacco cessation, like, yoga, hypnosis,
herbal products, acupuncture, relaxation, and massage therapy have been
tried and were successful. However, use of complementary and alternative
medicine treatments and a higher level of education were significantly
associated. Yoga and mindfulness meditation as promising complementary
therapies for treating and preventing addictive behaviors. The
hypothetical models propose that the skills, perceptions, and
self-awareness adapted through the practice of yoga and mindfulness can
target multiple psychological, physiological, neural, and behavioral
processes that maybe associated with relapse due to addiction.
Electronic cigarettes:
Also, electronic cigarettes are becoming popular and being debated
concerning their role in smoking cessation. The electronic cigarettes
are similarly known as e-cigarette, which is electronic nicotine
delivery system a mechanical device designed to mimic regular
cigarettes, looks conventional alike cigarette, and delivers nicotine
through inhaling vapors without burning tobacco. These devices are
supposed to deliver nicotine without any toxins considered to be a safer
alternative to regular tobacco cigarettes. However, there are no
sufficient studies to determine the vapors generates from e-cigarettes
don't contain any toxic substances harmful to health in contrast to the
natural tobacco smoking which has been proved to be carcinogenic. These
electronic devices sold as a tobacco delivery device needs to be
regulated. Currently, there are no uniform regulations, either no
regulations or at some places complete ban on sale. Countries like
Canada, Mexico, Israel, Brazil, Hong Kong, Panama, Singapore and the
United Arab Emirates have completely banned e-cigarettes. Subsequently,
more practical approaches are needed to reduce the burden of cigarette
smoking.
E-cigarettes were used much by former smokers to avoid relapse or as
an aid to cut down or quit smoking as the second option to nicotine
replacement medications. Based one-cigarette literature review, it was
found that electronic devices sold as a nicotine delivery device, need
further research to gather scientific evidence of their safety, efficacy
of device in delivering nicotine and other substances, patterns of use,
effectiveness for smoking cessation or quitting, prevention of relapse,
and issues associated regulations with the use of e-cigarettes. Many
studies have shown that smoking e-cigarette is harmless compared to
smoking traditional cigarettes. Most of the devices contain nicotine and
inhaling their vapors exposes users to toxic substances, including
lead, cadmium, and nickel, heavy metals that linked with significant
health problems Grana.
The electronic cigarette which resembles a conventional cigarette is a
battery-operated electronic device that is designed to vaporize a
liquid solution. The solution is known to contain propylene glycol and
or vegetable glycerin in which nicotine or other fragrances may be
dissolved. During puffing activates the lithium-ion rechargeable battery
that is designed to vaporize nicotine to be inhaled. The modern
e-cigarette was invented in the year 2003 by a Chinese scientist Hon
Like (Figure1, 2).
Figure 1.
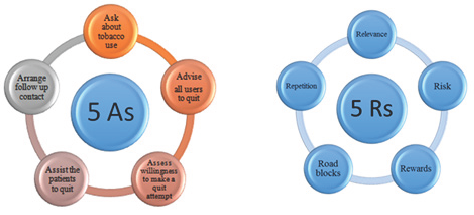
Figure 2.
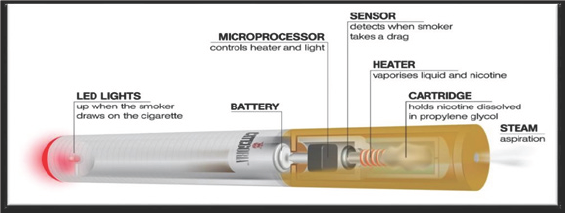
Even though e-cigarette bears a resemblance exactly as the
traditional conventional tobacco cigarettes has a perceptible sensation.
An e-cigarette consists of a plastic tube, electronic heating element,
and liquid nicotine cartridge. The conventional cigarette is soft and
light in weight whereas e-cigarette is hard and heavy to feel. The
e-cigarette is designed to mimic conventional cigarette provide a flavor
and physical sensation like that of tobacco smoke during inhalation,
but no smoke is involved in maneuvering.During the inhalation process in
e-cigarette device, an electronic sensor senses airflow and
automatically activates the heating element that heats the liquid in the
cartridge which vaporizes. Also at the same time during puffs, the
electronic sensor lights up a LED indicator. The cartridges may be
containing nicotine suspended in propylene glycol, glycerol plus water
and sometimes contains flavors of different fruits and mint or without
nicotine. The nicotine vapors absorb through the mucous membrane of
mouth may even enter into the blood stream, but with low concentration
comparing to conventional tobacco cigarettes. Since e-cigarettes don’t
burn tobacco, may be considered a lower risk substitute for conventional
paper and tobacco cigarette Eissenberg [18]. Toxic components,
including low levels of carcinogens have been identified in some
e-cigarette cartridges during laboratory testing Food and Drug
Administration [19].
Many scientific research studies have identified hundreds of toxic
chemicals used in the liquids in the canister of e-cigarettes were
detected in the bloodstream of some persons which inhaled by smoking
were known to cause health effects (may even cause cancer). Even persons
have affected second-hand smoke from e-cigarette have detected toxins
in the blood stream. The following chemicals are identified in
e-cigarettes: Nicotine, butanone, Formaldehyde, Acetaldehyde, Acetic
Acid, Acetone, Acrolein, Aluminum, Barium Benzene, Butyl hydroxyl
toluene, Cadmium, Chromium, Copper Croton Aldehyde Diethylene Glycol,
Glyoxal Iron Isoprene, Lead, Limonene m, p-Xylene, Magnesium, Manganese,
Nickel, N-Nitrosonornicotine, Methyl benzaldehyde, Phenol, Polycyclic
Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Potassium Propanol, Propylene Glycol, Sulfur,
Tin, Toluene, Vale Aldehyde, Zinc Zirconium.
There are numerous unreciprocated questions about their comprehensive
influence. For example; are e-cigarette used by young new non-smokers;
would e-cigarettes be a gateway to tobacco use or nicotine dependency;
is there any tendency for addiction to e-cigarettes or could its use in
public places challenge smoke-free laws. The nicotine and other
chemicals found in e-cigarettes might harm brain development in young
persons and younger persons who start smoking are more likely to develop
a habit and are more prone to addiction. Young persons who have never
smoked or never tried smoking, when starts to use e-cigarette might get
an addiction to nicotine and decide to switch to regular cigarettes is
the biggest worry and public health concern, if the government does not
ban e-cigarette sale to underage (Jean-Fran^ois Etter, 2011).
Smoking cessation policies and interventions
Smoking cessation is vital to any tobacco control program. It is also
one of the important modules of a widespread tobacco policy that
strongly contributes to decreasing the smoking prevalence and thereby
reduces tobacco-related morbidity and mortality. Numerous policies
influence smokers' inspiration to quit smoking. The tobacco control
measures such as increased taxation on tobacco and tobacco products, ban
on advertising and promotion by global communications media, smoke-free
areas and educational campaigns increase smokers’ motivation to stop.
These policies also help in creating a climate that makes it easier for
former smokers to remain abstained World Health Organization [20]. An
international body of research indicates smoking cessation policies and
interventions are cost-effective that include two comprehensive types of
activities:
a) Mass population policies and actions aimed to motivate smokers to
quit smoking, such as higher prices through taxation, restrictions on
smoking in public places and mass media educational campaigns.
b) 2) Policies and activities designed to help dependent smokers who are already motivated to quit Fronczak [21].
In May 2010, a committee of 20 experts from 12 countries on tobacco
control, economics, epidemiology, and public health policy met at the
International Agency for Research on Cancer Frank [22]. They discussed
the series of evidence gathered after conducting studies on the tobacco
pricing and tax related lobbying; tax, price and collective demand for
tobacco; tax, price and adult tobacco use, use among adolescents and
among poor; and impact of tobacco taxation on health. All the studies
were conducted in both the developed and underdeveloped countries
including high, medium and low income. From eighteen total studies,
twelve study’s conclusions were showing strength of the effectiveness on
tax reduction and price increase. A small number of high-income group
countries report that higher prices increased smoking cessation rate.
Studies from countries of low, medium and high income report that
smoking among young people decreases as price increases. After
consensus, the expert scientists’ committee concluded that there is
sufficient evidence of effectiveness of increased tobacco excise taxes
and prices in reducing the prevalence of tobacco use and improvement of
public health.
Uruguay, a middle-income country in South America, implemented a
comprehensive continued program of multiple tobacco control procedures
consisting of a ban on publicity and promotion. Additionally, the ban on
smoking in enclosed public spaces and workplaces, the policy for
healthcare providers to treat nicotine dependence. Furthermore, a rule,
that signs with warnings cover eighty percent of the front and back of
every cigarette pack in addition to the ban on using misleading terms
such as light and mild, besides a considerable increase in tobacco
taxes. The results reported over during six years' period from 2005 to
2011 was about a 23% decrease in tobacco use Abascal [23]. According to a
Global Youth Survey (GYT) from Bangladesh, a low-income country in
Asia, report between 2007 and 2013, the use of tobacco and its products
has not decreased. The rationale being no good smoking cessation
programs and lack of resources and insufficient policies on tobacco
control. This is despite many students (59.9%) expressing the desire to
quit smoking if they have proper guidance and tools World Health
Organization [24].
Brazil, an upper middle-income country, being a third largest tobacco
producing country in the world, has a comprehensive tobacco control
policy including restrictions on publicity, ban on smoking in indoor
public areas, mandatory pictorial warning labels on cigarette packs and
total ban on menthol cigarettes, increase tax and pricing policies. One
study showed that increase taxes and price rise have great potential to
stimulate cessation and reduces prevalence among the vulnerable
population Gigliotti [25-75].
Conclusions
This review suggests the trends of smoking habits and smoking
cessation intervention strategies differ from region to region when
viewed from an international perspective. This highlights the necessity
for the improvement of new methods that prevent people from starting to
smoke, motivate to quit smoking and sustain longterm cessation. Further,
we suggest exploring how to change more smokers to try quit and to
choose the most appropriate evidence- based practical approach and to
try more frequently. If appropriate and applicable, poly pharmacotherapy
should be offered for a prolonged period since relapse is more common.
Cessation programs must be custom-made to focus on the envisioned
audience rather than just providing information. It is observed by many
that e-cigarette to be harmless than traditional cigarettes, still a lot
of the devices contain nicotine and inhaling their vapors exposes users
to toxic substances, including lead, cadmium, and nickel, heavy metals
that linked with significant health problems (Grana, 2014).In developing
countries due to lack of infrastructure, and funds are the major
drawback towards the success of smoking control and smoking cessation,
rich countries should extend help in the implementation of intervention
programs. Additionally, countries can also contribute by strictly
implementing taxation on cigarettes and also increase the price of
tobacco and tobacco products in general. Future research should be
directed to assess whether increasing the number of quitting attempts
would positively impact smoking cessation.
Read More About Lupine Publishers Journal of Respiratory & Skin Diseases Please Click on Below Link:
https://lupine-respiratory-skin-and-diseases.blogspot.com/